Figure 7.
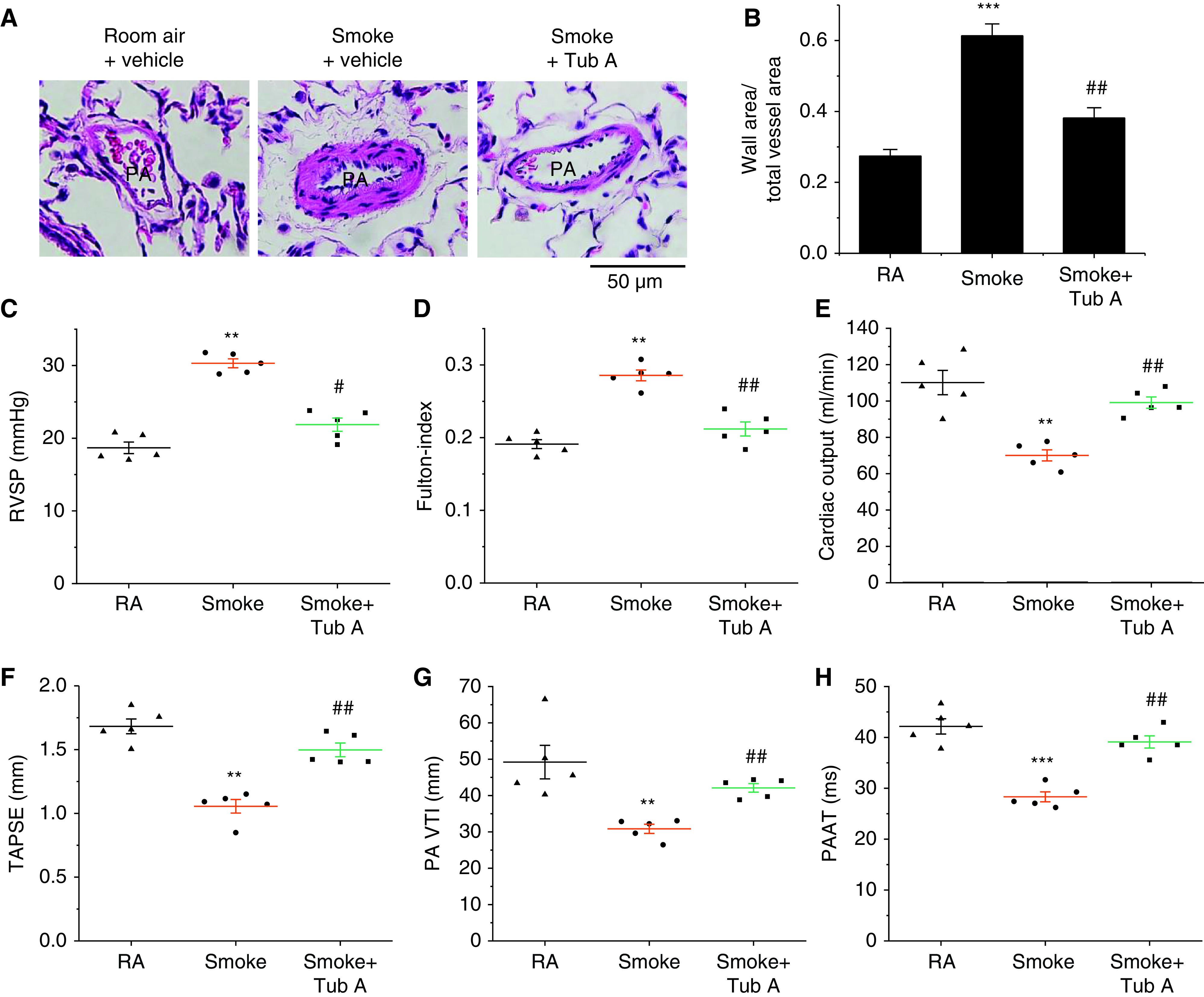
Tub A mitigates the progression of pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension in a CS-induced COPD model. Eight-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to CS for 16 weeks. At the beginning of the 14th week, CS-exposed rats were injected with Tub A (25 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle 5 d/wk for 3 weeks, and then echocardiographic findings, the extent of pulmonary vascular remodeling, and the extent of pulmonary hypertension were assessed. (A) Representative images of lung sections of rats exposed to RA or CS. (B) Changes in the ratio of the vessel wall area to the total vessel area. (C) Changes in RVSP. (D) Changes in the Fulton index [right ventricular weight/(left ventricular weight + septal weight)]. (E–H) Echocardiographic cardiac output, TAPSE, PA VTI, and PAAT results. Results are expressed as means ± SEs; n = 5. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. RA. #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01 vs. Smoke. PAAT = PA acceleration time; TAPSE = tricuspid annulus plain systolic excursion; RVSP = right ventricular systolic pressure; VTI = velocity–time integral.
