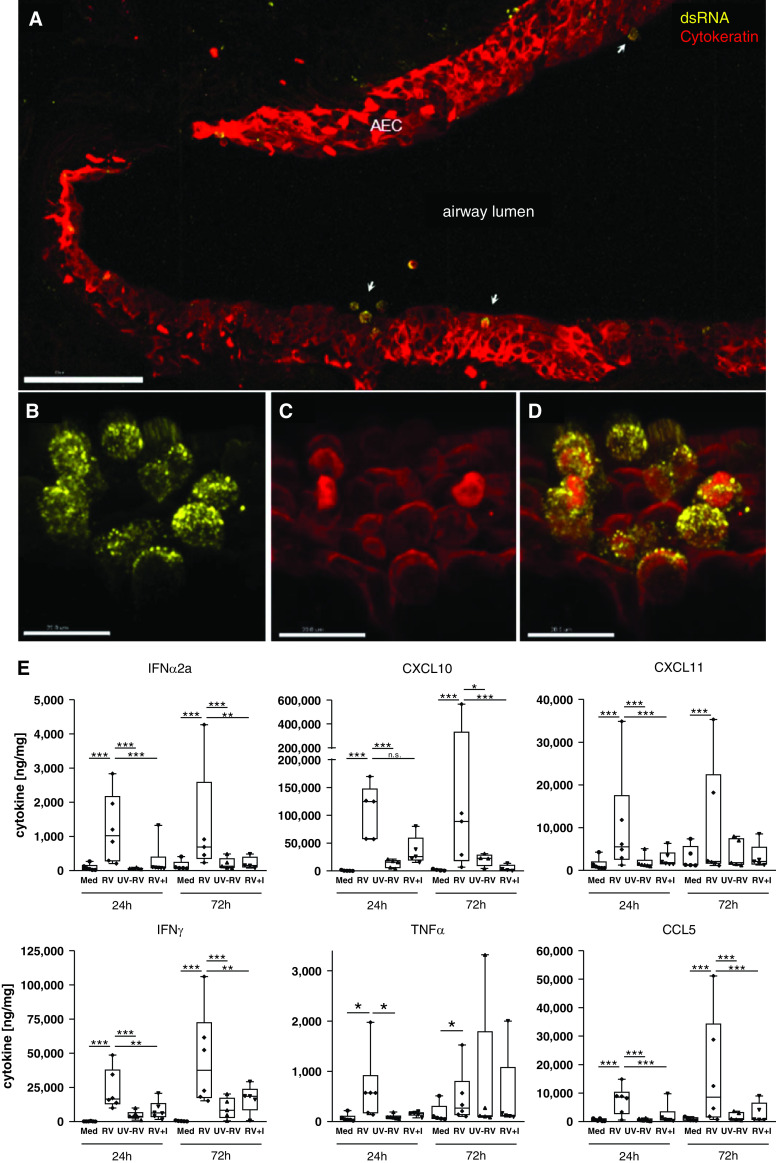
Figure 1.
Rhinovirus infects airway epithelium and elicits antiviral and proinflammatory host immune responses. (A–D) Replication of rhinovirus (RV) 1B in viable human lung tissue was detected by dsRNA staining (yellow) (A, B, and D), and localization within AEC was confirmed by staining of pan-cytokeratin (red) (A, C, and D). Three-dimensional images: scale bars: A, 100 μm; and B–D, 15 μm. (E) Proinflammatory and antiviral cytokines were detected by human 7-plex tissue culture kit from MesoScaleDiscovery after RV infection with and without antiviral treatment (I, 100 nM rupintrivir) as compared with Med and UV-RV. Cytokine release from lung tissue is displayed in ng cytokine/mg whole protein content. Box and whisker plots show median, 25th and 75th percentiles, and minimum and maximum values, showing all data points. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, and ***P < 0.001 according to linear mixed-effects model and false discovery rate method as detailed in the online supplement. N = 5–6 donors, with duplicate precision-cut lung slices per condition. AEC = airway epithelial cells; dsRNA = double-stranded RNA; I = inhibitor; Med = medium; UV-RV = ultraviolet-inactivated RV control.