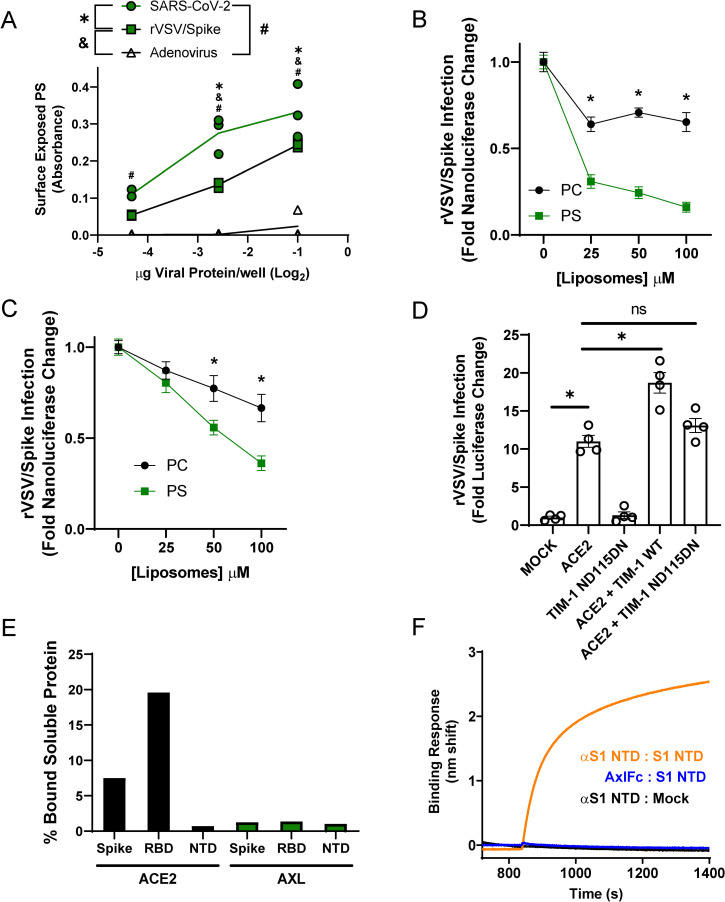
Fig 2. PS receptors interact with SARS-CoV-2 by binding to virion PS.
A) PS is readily detectable on UV irradiated SARS-CoV-2 virions and rVSV/Spike. Indicated quantities of viral particles (determined by protein content) were coated in ELISA plates, and PS was detected using bavituximab followed by secondary antisera. B-C) PS liposomes interfere with rVSV/Spike infection. HEK 293T cells transfected with 50 ng of ACE2 plasmid and 1 μg of TIM-1 (B) or AXL (C) plasmid. Cells were infected with rVSV/Spike in the presence of increasing concentrations of PS or PC liposomes and assessed for nanoluciferase activity 24 hours later. D) HEK 293T cells were transfected with 1 μg of plasmid expressing WT or PS binding pocket mutant TIM-1 (ND115DN) with or without 250 ng of ACE2 plasmid and infected 48 hours later with rVSV/Spike. Luminescence fold change were compared to Mock transfected lysates that were set to a value of 1. E) Surface expressed AXL is unable to directly interact with purified SARS-CoV-2 spike/Fc proteins. HEK 293T cells transfected with AXL or ACE2 were incubated with soluble Spike protein-Fc, S1 RBD-Fc or S1 NTD-Fc and subsequently incubated with an Alexa 647 secondary against Fc. Transfected cells bound to spike constructs were detected by flow cytometry. F) Purified AXL does not bind to the NTD of SARS-CoV-2 spike. Biolayer interferometry association curves show that immobilized AXL-Fc fails to interact with purified NTD of spike. Data are pooled from at least 3 independent experiments (B, C) or are representative of at least 3 experiments (A, D, E, F). Data represented as means (or individual datapoints) ± SEM. Multiple t-test (B, C), One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons (A, D); asterisks represent p < 0.05.