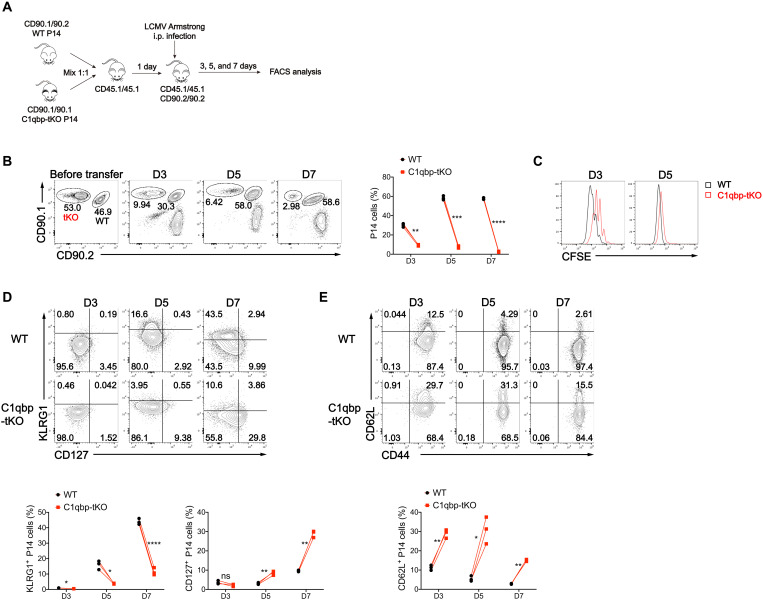
Fig. 3. C1qbp is intrinsically required for proliferation and differentiation of effector CD8+ T cells.
(A) Schematic of P14 cotransfer experiments. i.p., intraperitoneal; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting. (B) Flow cytometry of splenic CD8+ T cells (left) and frequency of donor P14 CD8+ T cells (among splenic CD8+ T cells) (right) from B6.SJL recipient mice given transfer of naïve WT (CD90.1/CD90.2) and C1qbp-deficient (CD90.1/CD90.1) P14 CD8+ T cells, followed by infection with the LCMV Armstrong strain and analysis at indicated days after infection as in (A) (n = 3 per group). (C) Proliferation of donor WT and C1qbp-deficient P14 CD8+ T cells from recipient mice as in (A), indicated by flow cytometry of carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE) dilution. (D and E) Flow cytometry of donor WT and C1qbp-deficient P14 CD8+ T cells and frequency of KLRG1+ (D, bottom left) or CD127+ (D, bottom right) or CD62L+ (E) P14 CD8+ T cells (among donor P14 CD8+ T cells) from recipient mice as in (A) (n = 3 per group). Each symbol represents an individual mouse; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 (two-tailed paired Student’s t test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (error bars, SD).