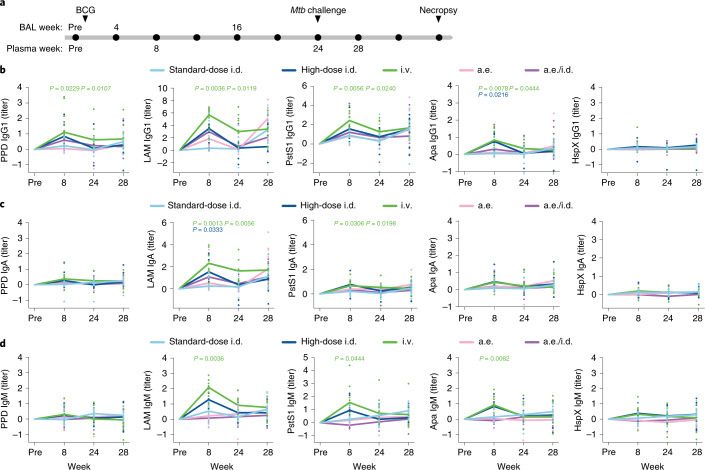
Fig. 1. Intravenous BCG-immunized macaques exhibit higher and more durable plasma antibody titers.
a, Timeline of the original vaccination study indicating the samples available by compartment. Week 12 rather than week 16 BAL samples were analyzed in four of eight macaques in the high-dose i.d. group. BAL samples from all remaining macaques were analyzed at week 16. b–d, Fold change in IgG1 (b), IgA (c) and IgM (d) titers present in the plasma of each rhesus macaque following BCG vaccination. Fold changes were calculated as fold change in Luminex median fluorescence intensity (MFI) over the pre-vaccination level for each macaque. A base-2 log scale was used for the y axis. Each point represents the duplicate average from a single macaque. The lines show group medians over time. Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s multiple-comparison tests were performed on the fold change values at each time point, comparing each experimental BCG vaccination group to the standard-dose i.d. BCG group. Adjusted P values < 0.05 compared to the standard-dose i.d. BCG group are shown and are colored by vaccination group.