Figure 1. Developing Brain Microglia “Report Card” Across Culture Models.
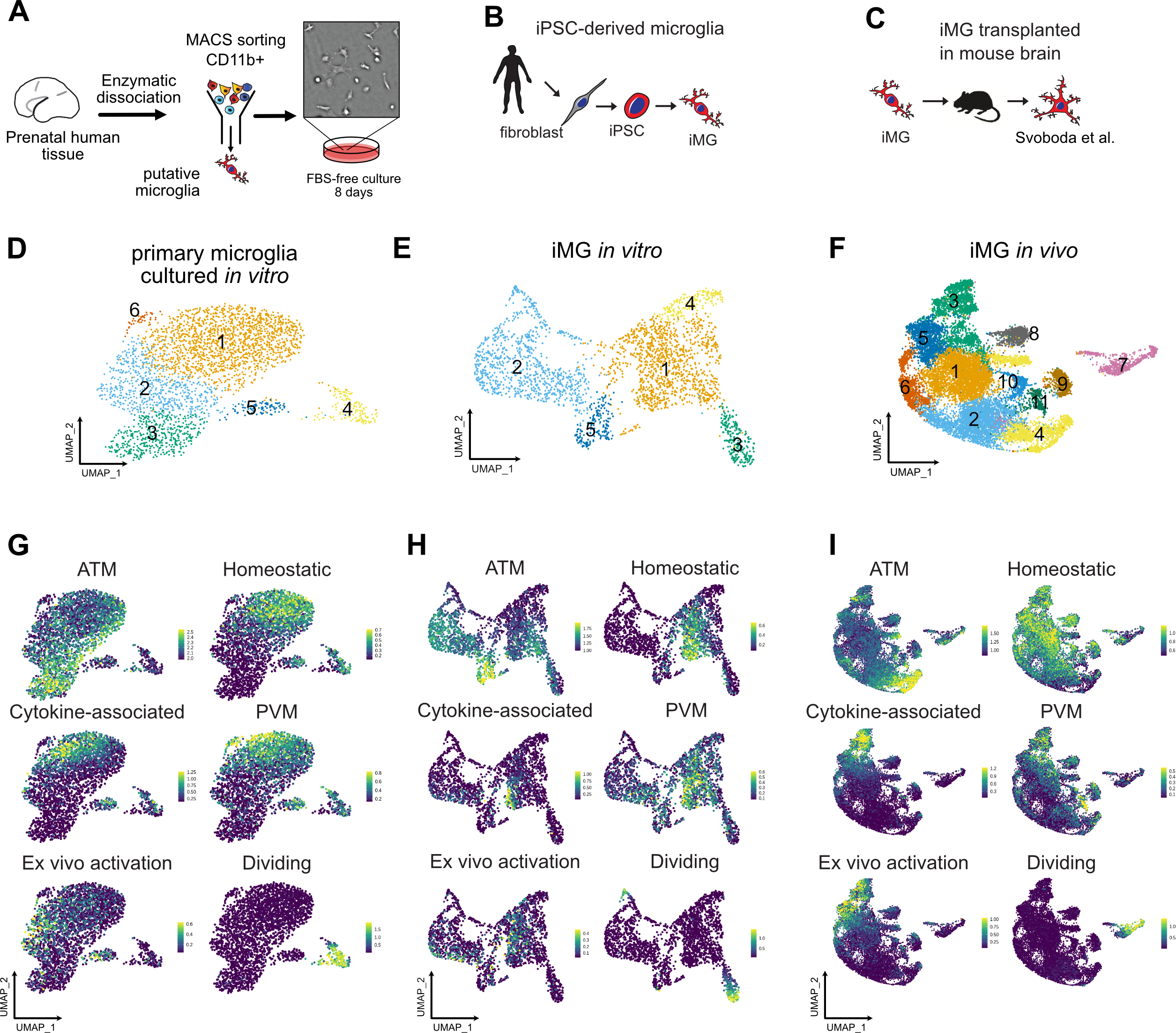
A. Primary human microglia were extracted from the mid-gestation human brain. The tissue was enzymatically dissociated with papain, MACS-sorted with Cd11b magnetic beads-conjugated antibody and cultured in defined media for 8 days. B. Microglia from induced pluripotent stem cells as a reliable microglia source. N=1 (iCell Microglia, cat#01279). C. A schematic for induced microglia transplanted into the mouse brain (from (Svoboda, Barrasa et al. 2019). D. UMAP plot of 2,970 microglia after 8 days of in vitro culture reveals five microglia clusters. N=1 brain sample (GW23 primary cortex). See also Figure S1. E. scRNAseq identifies six molecular clusters among induced microglia cells. 2,659 induced microglia (iMG) cells from N=1 experiment were used. F. scRNAseq identifies eight molecular clusters among induced microglia cells “cultured” in the mouse brain. 15,971cells from N=4 mouse brain samples 60 days post-injection were used, as previously described (Svoboda, Barrasa et al. 2019). G, H, I. Scores for individual microglia clusters for primary human microglia from Figures S1–2 were calculated and projected onto gene expression space for each microglia model. Individual genes used to calculate model scores are in Figure S2. ATM – axon tract associated microglia (with high expression of LGALS/LGALS3, APOC1, SPP1); homeostatic microglia – cluster with high expression of CX3CR1, P2RY12/P2RY13, VSIR, IFNGR1; cytokine-associated microglia – cluster with high expression of CCL3/CCL4, CXCL8, IL1B, TNF; PVM – perivascular macrophages (characterized by high expression of F13A1, MRC1, LYVE1, LYZ); Ex vivo activation – microglia cluster with high expression of genes associated with cell stress during enzymatic cell dissociation (JUN, HSPA6/HSPA1A, DUSP1, FOS); dividing cells – cells characterized by cell cycle genes (TOP2A, MKI67, CENPF).
