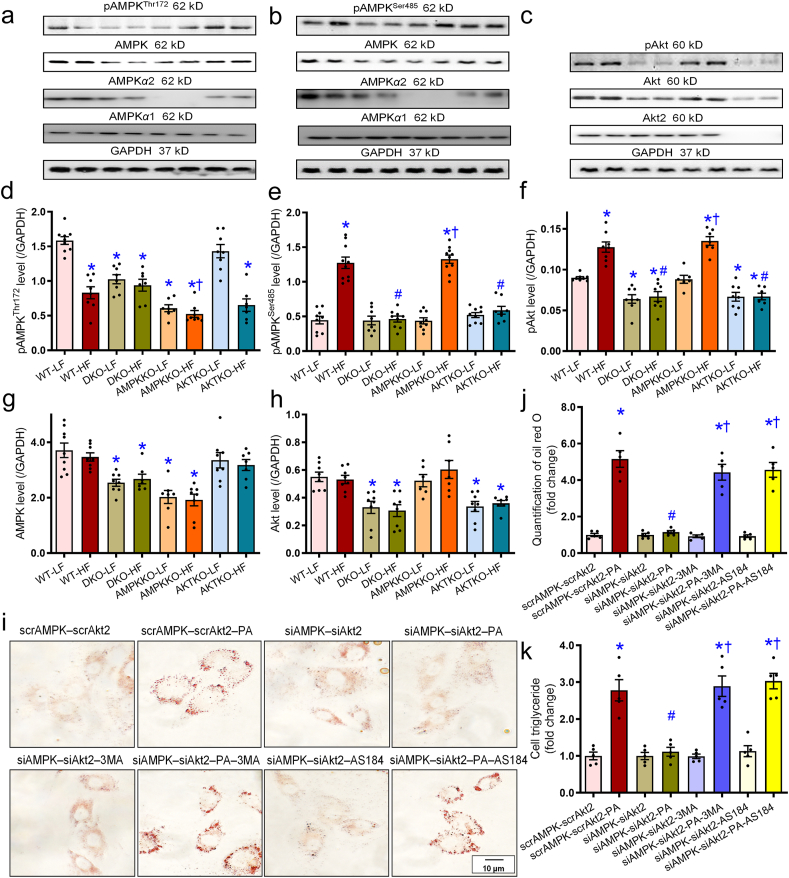
Figure 9.
Effect of Ampkα2−/−, Akt2−/−, and DKO on pan- and phosphorylated levels of AMPK and Akt in mice livers and the effects of Ampk and Akt2 knockdown on palmitic acid (PA)-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. (a–c) Representative gel blots of panels d–h depicting pan- and phosphorylated AMPK and Akt as well as AMPKα1, AMPKα2, and Akt2 subunits using specific antibodies. (d) pAMPK (Th172)-to-GAPDH ratio. (e) pAMPK (Ser485)-to-GAPDH ratio. (f) pAkt (Ser473)-to-GAPDH ratio. (g) AMPK levels. (h) Akt level. (i–k) Cells were treated with scrAMPK-scrAkt2 or siAMPK-siAkt2 prior to exposure to PA (0.5 mmol/L) in the presence or absence of the autophagy inhibitor 3-MA (10 mmol/L) and the FoxO1 inhibitor AS1842856 (100 nmol/L) for 72 h. Representative oil red O staining images from the indicated HepG2 groups (i), quantification of oil red O (j), and cellular triglyceride levels (k) were shown. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 7–9 mice per group, panels a–h; n = 5 independent experiments, panels j and k). ∗P < 0.05 vs. WT mice or scrAMPK-scrAKT group; #P < 0.05 vs. WT-HF mice or scrAMPK-scrAKT-PA group; †P < 0.05 vs. DKO-HF mice or siAMPK-siAKT-PA group.