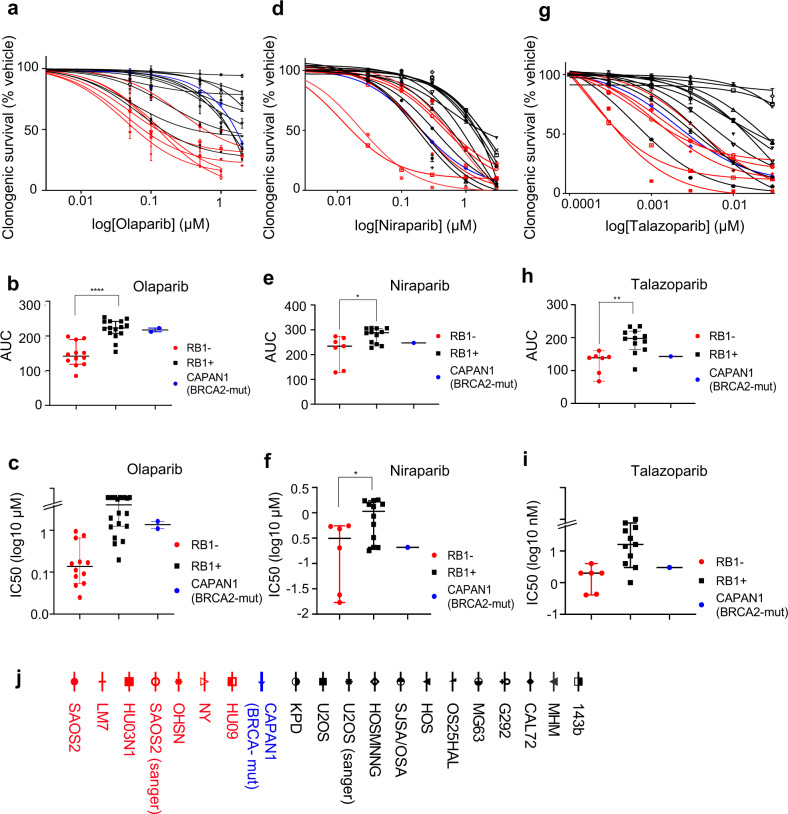
Fig. 2. Effect of PARP inhibition on clonogenic survival.
Cells were seeded at low density into six-well plates followed by treatment with increasing concentrations of PARP inhibitors or vehicle. Colonies arising were stained using crystal violet dye. Clonogenic survival was quantified using dye extraction. Clonogenic survival concentration-response curves for RB1-defective (red) or RB1-normal (black) osteosarcoma and BRCA2-mutant CAPAN1 (blue) after treatment with a olaparib, d niraparib, or g talazoparib. Data reflect the mean ± SD of parallel duplicates from one dataset. Scatter plots comparing AUC values for RB1-defective or RB1-normal osteosarcoma lines and BRCA2-mutant CAPAN1 treated with b olaparib, e niraparib or h talazoparib summarising data for n = 2 (b) or n = 1 (e, h) biologically independent dataset. Bars depict median ±95% CI. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 calculated using two-tailed Mann–Whitney tests, p (b) < 0.0001, p (e) = 0.022 and p (h) = 0.0012. c, f, i Scatter plots depicting IC50 values deduced from dose response data in b, e and h. Bars depict median ±95% CI; p (f) = 0.032*, calculated using two-tailed Mann–Whitney tests. j Symbols and names for cell lines used. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.