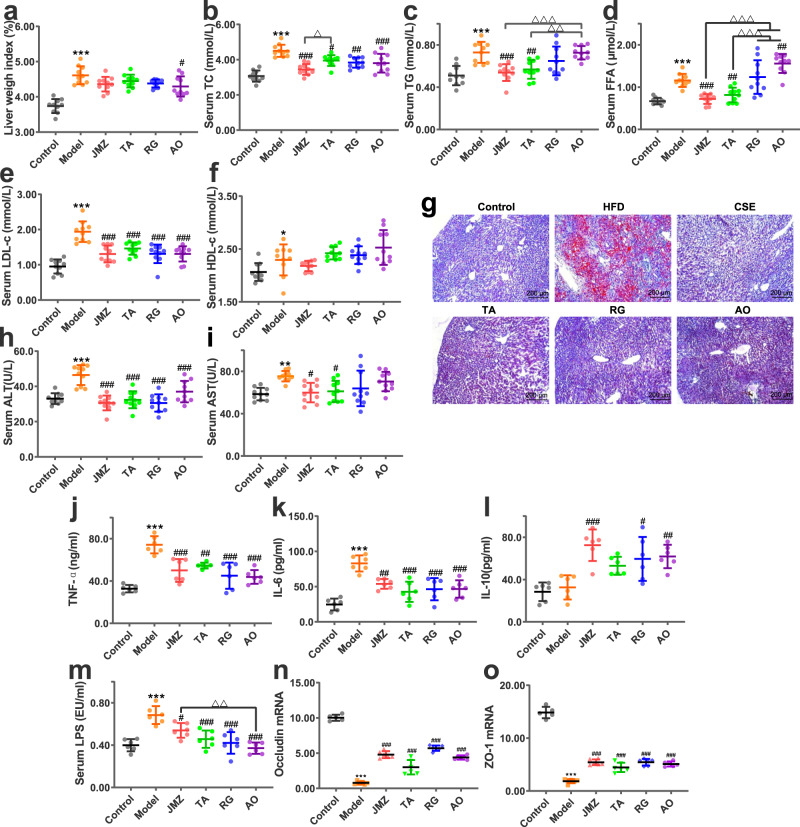
Fig. 2. CSE (10 g/kg), total aglycone (TA) (10 g/kg), RG (20 mg/kg) and aurantio-obtusin (AO) (20 mg/kg) ameliorated liver weight indices and fat accumulation, liver injury and inflammation, intestinal mucosal barrier injury and altered microbiota diversity in HFD-fed mice.
Data for liver weight indices (a), serum total cholesterol (TC) (b), triglycerides (TG) (c), free fatty acids (FFA) (d), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) (e), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) (f), n = 10 mice/group. Liver lipid accumulation. Liver tissue was stained with oil red O and observed under light microscopy (100×) (g). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (h) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (i) levels reflect the effects of HFD and administration on liver injury in mice, n = 10 mice/group. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (j), interleukin (IL)-6 (k), and IL-10 (l) levels reflect liver inflammation, n = 6 mice/group. Serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels (m), occludin and zonula occludens (ZO) −1 mRNA relative expression (n, o), n = 6 mice/group. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analyses were performed using Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. HFD; △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.01, △△△P < 0.001.