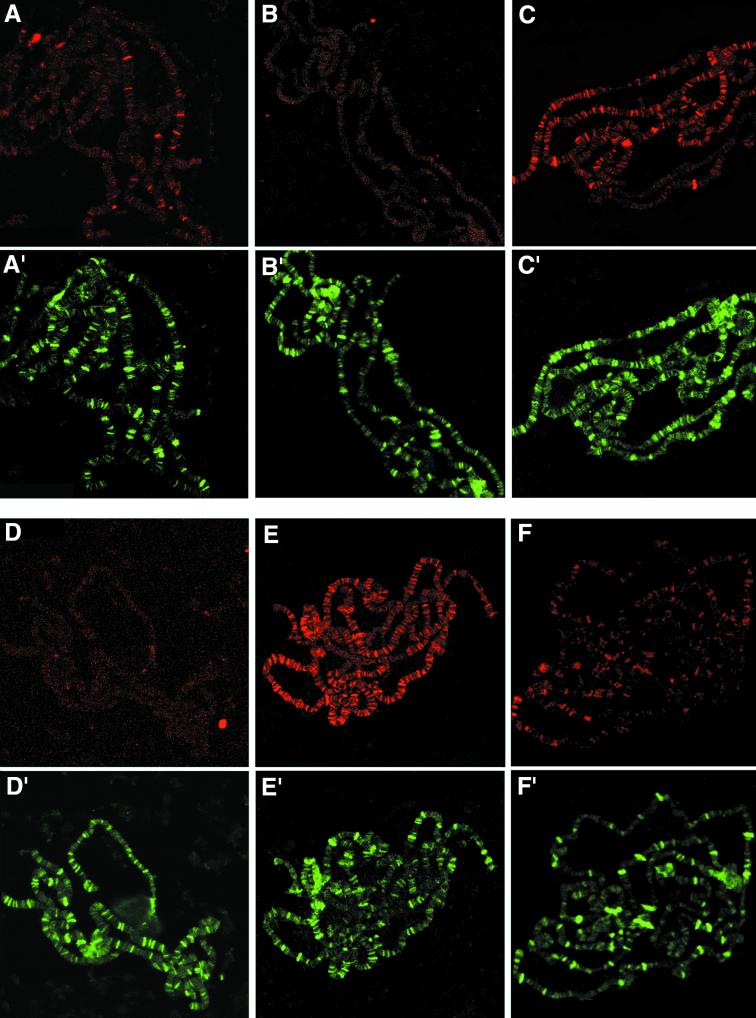
FIG. 4.
Immunolocalization of SU(S) ARM mutant derivatives on third-instar larval salivary gland polytene chromosomes. Shown are confocal images of chromosome squashes double labeled by indirect immunofluorescence with antibodies that recognize SU(S) and the positive control HRP36. The pseudocolored images indicate SU(S) in red (A to F) and HRP36 in green (A′ to F′). HRP36 is found at a much larger number of bands than endogenous SU(S), and there is little overlap between strong HRP36 sites and strong SU(S) sites. (A and A′) su(s)+; (B and B′) su(s)R39 null mutant. The remaining images were prepared from larvae grown at room temperature, expressing an SU(S) cDNA transgene under control of the hs-GAL4 driver in su(s) null mutant background: (C and C′) SU(S)wt; (D and D′) SU(S)ΔARM1; (E and E′) SU(S)ΔARM2; (F and F′) SU(S)ΔARM1,2.