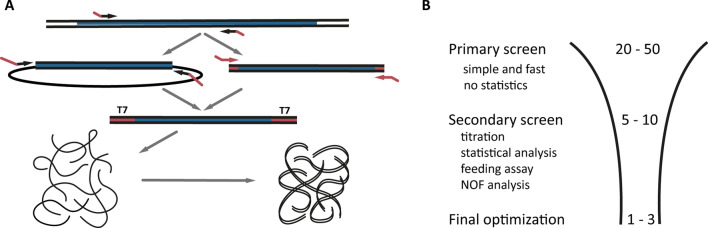
Fig. 1.
Workflows for dsRNA production and target gene screening. a A 500–1000 bp fragment of the target gene is amplified from genomic DNA or cDNA. Either, the fragment amplified with gene specific primers (black arrows) and cloned into a vector and confirmed by sequencing. Alternatively, linkers are attached to the primers (red part of the primers) and the PCR product is gel purified, sequenced and kept as stock. In both cases, primers that contain a T7 promoter sequence (red parts of arrows) are used to amplify the sequence in a secondary PCR. This PCR is used for in vitro transcription leading to a mixture of annealed and non-annealed RNA (left part). An annealing procedure enriches for double stranded RNAs. b Given the variability of orthologs to serve as good RNAi target genes for pest control, it is recommended to test a large number of genes in a primary screen, which is optimized for fast throughput. A small number of the best candidates is then further scrutinized by titration assays including statistical analysis, feeding assay and off target control using non-overlapping dsRNA fragments (NOF). Final optimization of the fragment might increase efficacy and safety in the field