Figure 1. NLRP6 Interacts with dsRNA in Vitro.
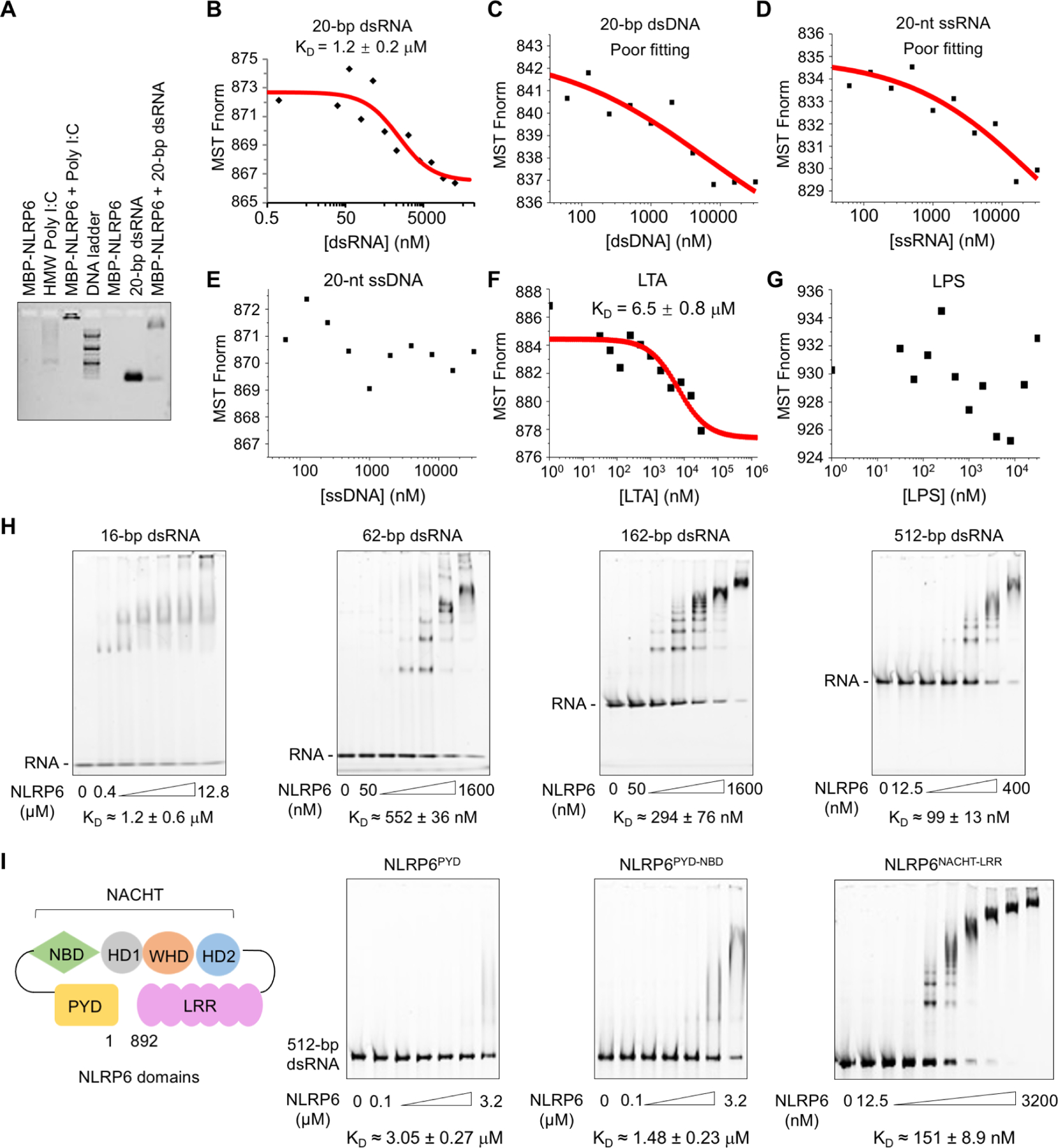
(A) Agarose gel-shift assay of HMW poly I:C and 20-bp dsRNA with MBP-tagged NLRP6. HMW poly I:C alone ran as a smear.
(B–E) Measurements of dissociation constants (KD) of NLRP6 with different types of nucleic acids by microscale thermophoresis (MST). Each KD was derived from the binding response as a function of the GFP-NLRP6 concentration. Errors in KD represent fitting errors.
(F, G) KD measurements of NLRP6 with different ligands (LTA, LPS) by MST.
(H, I) Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) of MBP-NLRP6 with dsRNA of different lengths at 2.5 ng/μL (H) and of different MBP-NLRP6 truncations with 512-bp dsRNA at 2.5 ng/μL (I). The MBP-NLRP6 concentrations were in two-fold dilutions and the first and last concentrations are shown. KD was derived from the free dsRNA Intensity as a function of the MBP-NLRP6 concentration. Errors in KD represent fitting errors.
See also Figure S1
