Fig. 2 |. Proposed mechanism and nitrogen-heterocyclic carbene evaluation for deoxygenative arylation.
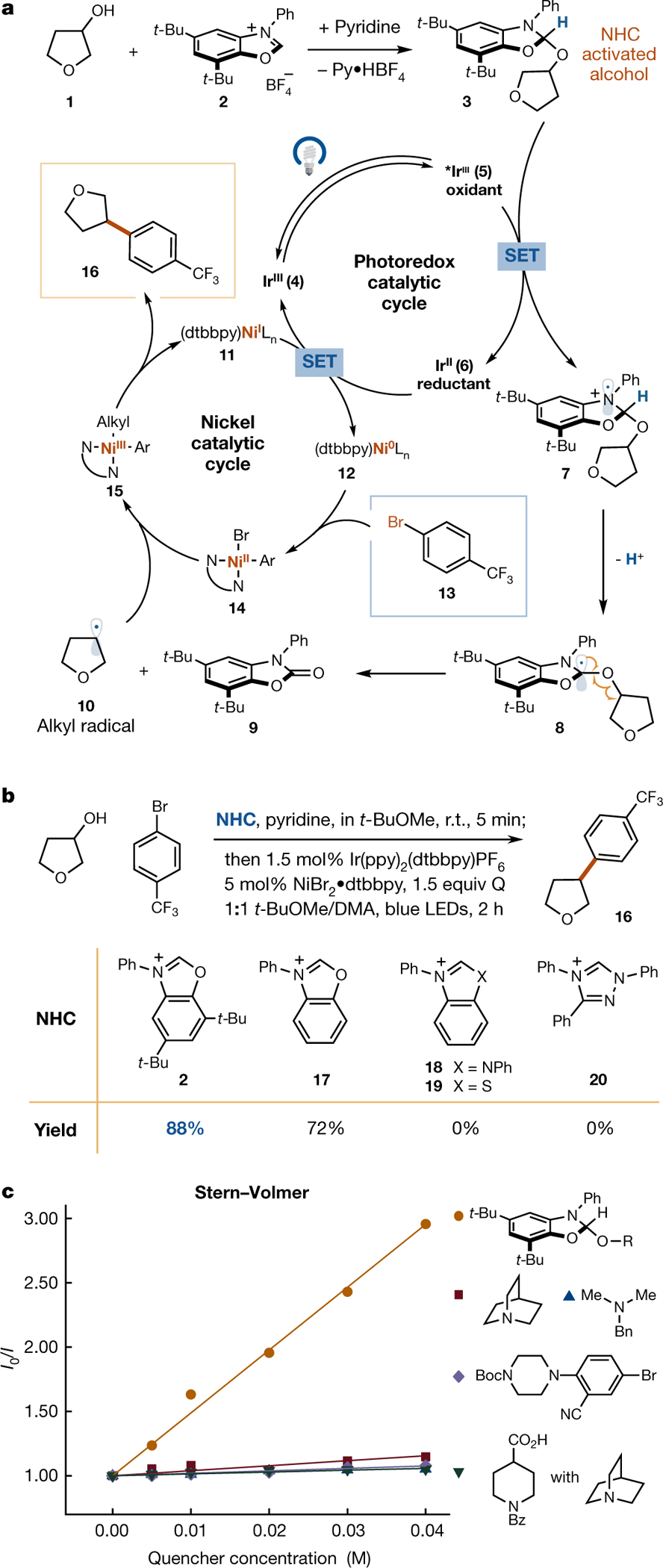
a, The starting alcohol 1 is converted to adduct 3 in the presence of NHC salt 2 and base. The deoxygenative radical 10 is generated from 3 upon sequential electron–proton transfer and followed by facile β-scission, which can be captured by Ni-aryl species 14 to yield the arylated product 16. b, Evaluation of N-heterocyclic carbene salts for deoxygenative arylation. For detailed optimization, see Supplementary Information. c, Stern–Volmer quenching comparison of NHC adduct 3 and other readily oxidizable functional groups. Py•HBF4, pyridinium tetrafluoroborate; Q, quinuclidine; t-BuOMe, methyl tert-butyl ether; DMA, dimethylacetamide; R, 3-tetrahydrofuranyl.
