Figure 3. Y3 induces UPR through activating AMPK in EOC cells.
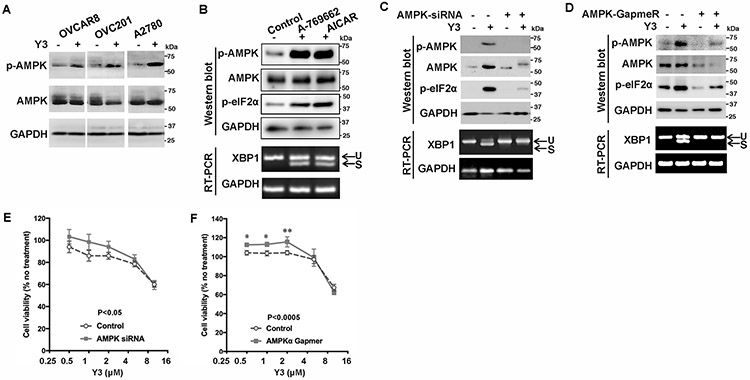
A, Representative images of western blot. Y3 induced AMPK phosphorylation in ovarian cancer cells. p-AMPK, phosphorylated AMPK. AMPK, total AMPK. GAPDH was used as a loading control. B, Representative images of western blot and agarose gel electrophoresis. A2780 cells were treated with AMPK activators A-769662 (10 μM) or AICAR (1 mM) for 24 h. Whole cell lysate was analyzed with western blot. The splicing of XBP1 mRNA was analyzed by RT-PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis. U, unspliced. S, spliced. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C, AMPK siRNA knocks down AMPK expression and inhibits Y3-induced eIF2α phosphorylation and XBP1 mRNA splicing. U, unspliced. S, spliced. GAPDH was used as a loading control. D, AMPK GapmeR knocks down AMPK expression and inhibits Y3-induced eIF2α phosphorylation and XBP1 mRNA splicing. U, unspliced. S, spliced. GAPDH was used as a loading control. E and F, AMPK siRNA (E) and GapmeR (F) partially inhibit the response of A2780 cells to Y3. Two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak HSD test, n=5, p values for the comparisons between the entire control and knockdown groups as indicated in the graph. *P<0.05 and **P<0.005 for comparisons between control and knockdown groups at the indicated concentrations.
