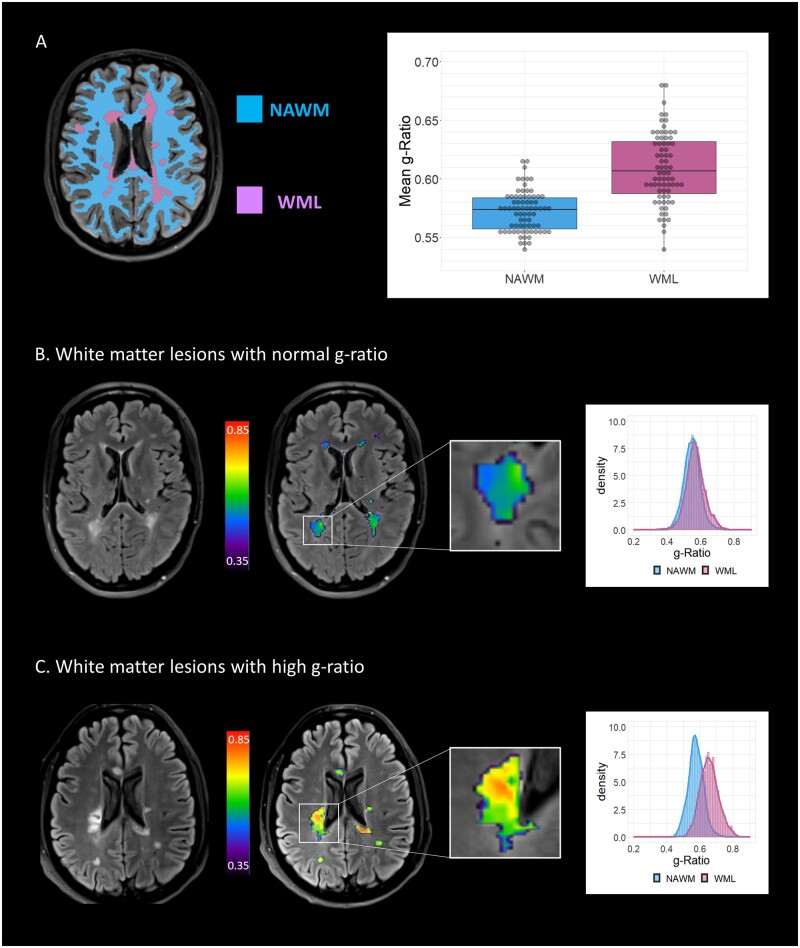
Figure 2.
G-ratio in cerebral white matter lesions at MS diagnosis. A shows segmentation strategy for anatomical MRI scans, dividing white matter into white matter lesions (WML, purple) and normal-appearing white matter (NAWM, blue). The g-ratio is increased in lesions compared to NAWM in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis patients (0.61 versus 0.57, difference: 0.036, 95% CI: 0.029–0.043, P<0.001 paired t-test). B shows representative patient with normal g-ratio within WML. On the left, the T2 Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery image is shown, with hyperintense WML consistent with multiple sclerosis. The aggregate g-ratio from these lesion segmentations was evaluated (right-hand MRI, g-ratio denoted by colour scale), leading to a histogram where the distribution of g-ratio values between NAWM (blue) and WML (purple) could not be distinguished. C shows representative patient with high g-ratio within WML. The lesion shown has a high g-ratio (right-hand MRI) and the resulting individual histogram from the patient shows separation of g-ratio distributions derived from NAWM (blue) and WML (purple).