Figure 1.
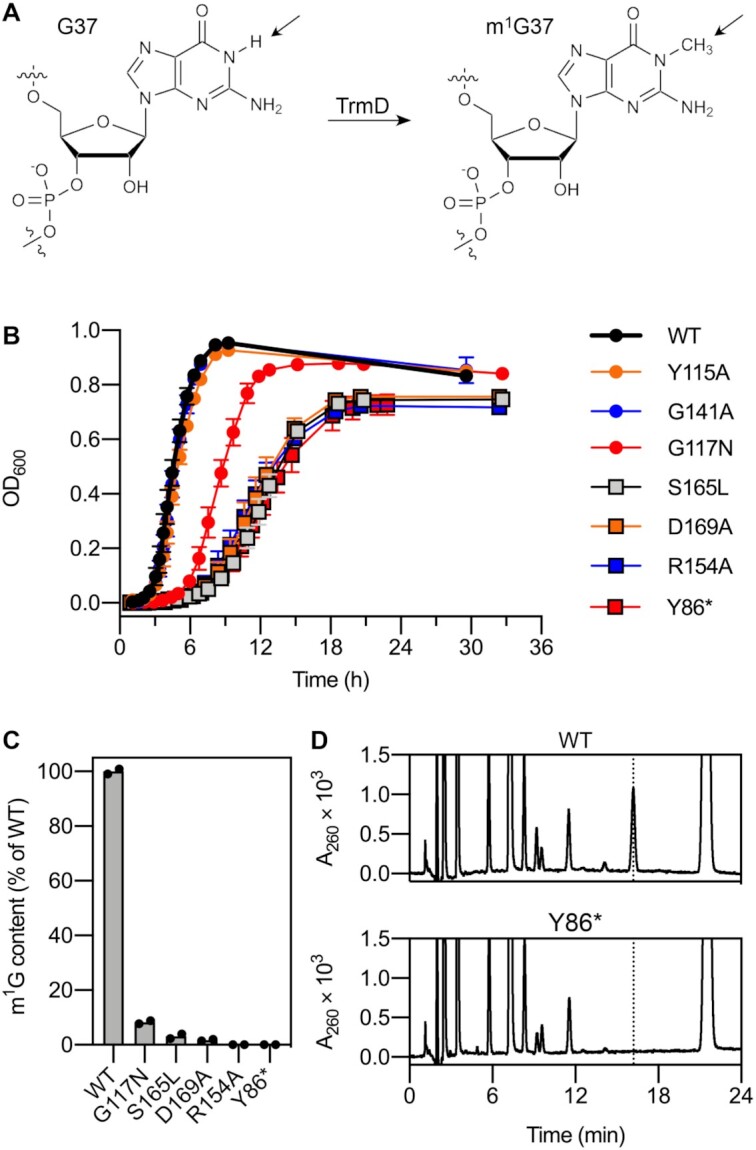
Characterization of E. coli strains with mutations in trmD. (A) N1-methylation of guanosine 37 catalyzed by TrmD. The arrows indicate the position of the modification. (B) Growth assays of trmD mutant strains in LB medium at 37°C. Data represent mean ± s.d.: WT, Y115A, n = 9 colonies; G141A, n = 5 colonies; G117N, R154A, Y86*, n = 4 colonies (three technical replicates per colony); S165L, D169A, n = 3 colonies (three technical replicates per colony). (C) m1G content in tRNAPro (CGG) purified from trmD mutant strains, determined by UPLC. m1G content was estimated by comparing the peak area ratio of m1G to pseudouridine in the A260 chromatogram between the WT and mutant strains. n = 2 biological replicates. (D) Separation of nucleosides in digested tRNAPro (CGG) by UPLC. UV chromatograms (260 nm detection) are shown for tRNA derived from the WT and Y86* strains. The peak at 16.198 min corresponding to m1G is indicated by the dotted line.
