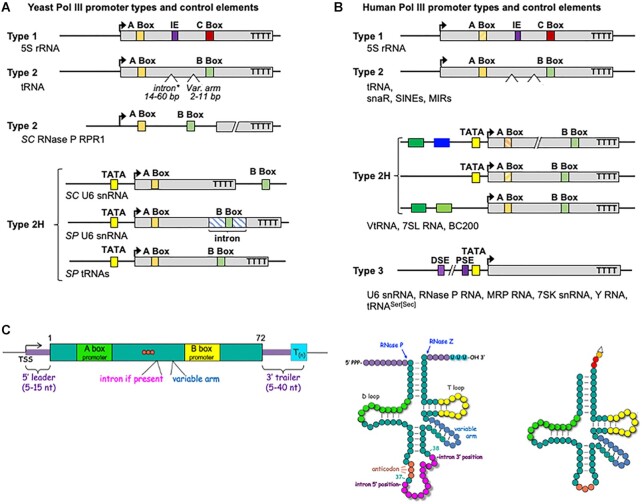
Figure 2.
The different promoter types used to direct transcription of Pol III-dependent genes in yeast and human. (A) The two promoter types of yeast are depicted along with the hybrid subtype 2H, as suggested by (41). Type 1 is conserved from yeast to human and limited to 5S rRNA genes. Type 2 promoters contain an A Box and B Box, the distance between which varies as tRNA genes contain extra arms of variable length, and a subset contain introns of variable length. Type 2H (hybrid) promoters are similar to type 2 with an A-Box followed by a B-Box and also contain an upstream TATA element at −30. Bent arrows indicate the transcription start sites (TSS). In yeast (SC, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, SP Schizosaccharomyces pombe) type 2H have unique variations of the A- and B- Box seen in type 2. For SC RPR1 (RNase P RNA) the promoter elements are found upstream of what becomes the mature RNA species. For U6 the B Box is outside the mature RNA in SC and within an intron in SP. Not shown is the SC scR1 gene schematic encoding SRP RNA which has a TATA beginning at −31 relative to +1 of scR1. (B) The three promoter types in human are depicted along with the 2H subtypes which vary in upstream control elements (41), notable for 7SL, BC200 and VtRNAs (colored boxes). The type 3 promoter is present in higher eukaryotes (not found in yeast) consisting of a proximal sequence element (PSE), a TATA box and a distal sequence element (DSE). A type 3 promoter type, comprised of elements that direct assembly of the transcription complex exclusively from upstream of the TSS, is not found in yeast. Regardless of the variable types of promoters that direct initiation, the control element that terminates transcription by the Pols III from yeast to human, is a short oligo(T) tract on the non-template strand. (C) Left: A schematized tRNA gene is illustrated with its variable hallmark features, color-coded according to the tRNA cloverleaf models to the right. These include the Pol III terminator, the 5′pppN TSS = transcription start site, 5′ leader, 3′ trailer, variable arm and intron between the A and B Boxes. Note that three orange circles represent the anticodon. Middle: General cloverleaf model of a nascent precursor-tRNA with an intron and variable arm and other segments color-coded with the gene diagram. The RNase P and RNase Z cleavage sites are indicated, as are the 5′ppp and 3′OH ends. A tract of Us at the 3′ end that results from termination is the sequence-specific binding site for the La protein, pre-tRNA chaperone/maturation factor. Right: Representation of a corresponding mature tRNA. Following splicing and processing, CCA is added to the matured 3′ end, after which the amino acid is attached (open triangle).