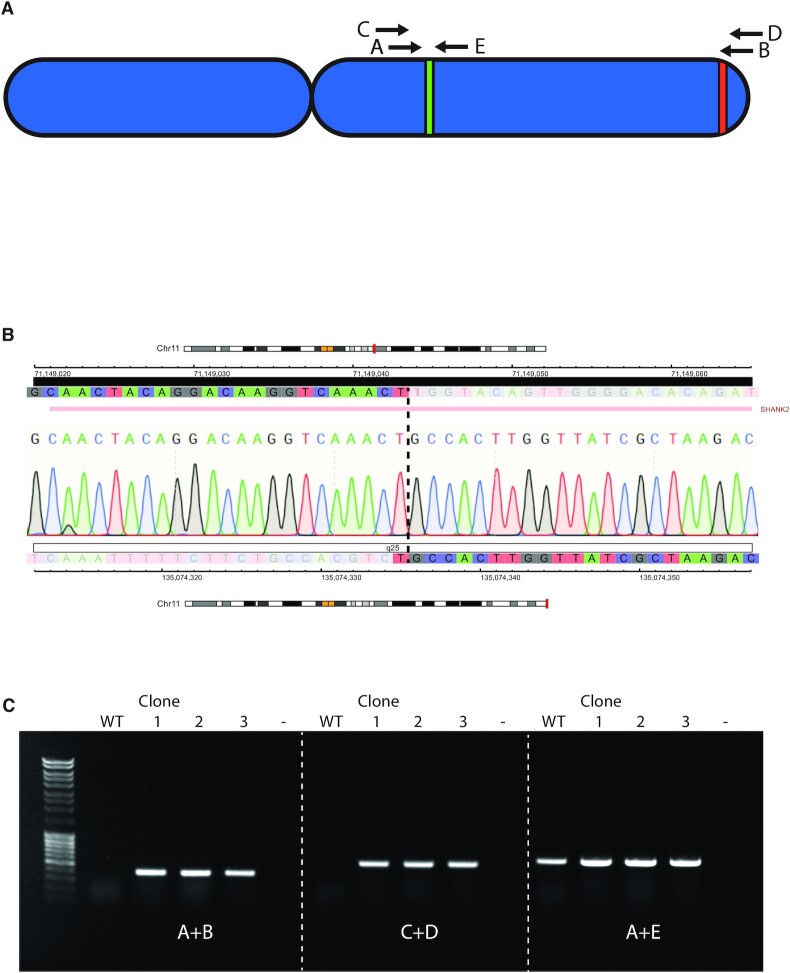
Figure 2.
PCR analysis indicates the presence of a translocation between 11q13.4 and 11q.25. (A) Schematic overview of chromosome 11, with green and red regions representing the regions adjacent to the gRNA recognition sites and letters representing primers used for analysis. (Table 1A) (B) Sanger sequencing electropherogram results of the translocation product from SKNSH 11q clone 4. Color coded tracks above and below the trace represent the sequence (C = blue, T = red, G = gray, A = green) genomic coordinates (HG19) and chromosomal location of the centromeric and telomeric region of the translocation, respectively. Ideograms representing the chromosomal location (shown in red), banding pattern (centromeres are represented in yellow). The gene located in the affected regions, i.e. the SHANK2 gene on the centromeric end, is shown above the profile. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the PCR reaction of the wild-type (WT) and the three clones (1, 2 and 3) from two experiments that were positive for the presence of a translocation. The first lane contains Generuler 1 kb DNA ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Primer combinations are shown below the bands and refer to the primers shown in (A).