Figure 3.
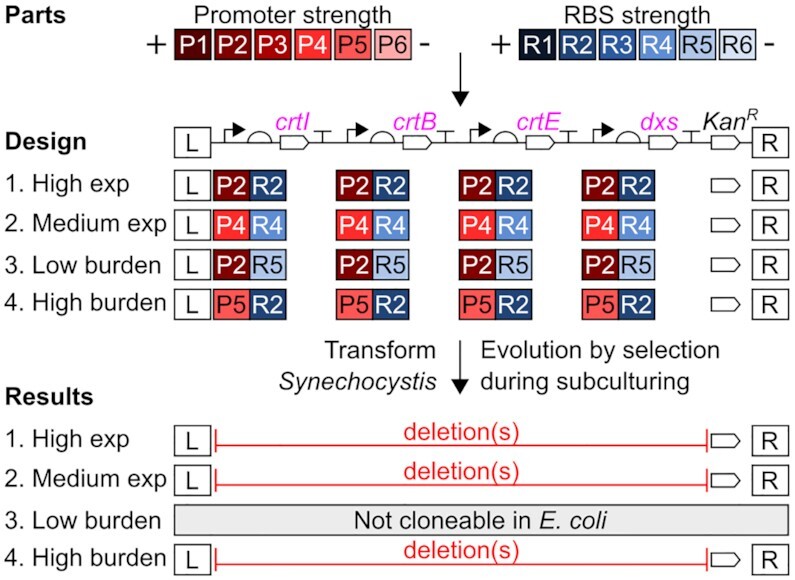
Rational design and genetic instability of individual lycopene overproduction constructs for Synechocystis. Four individual pathway constructs were designed: high expression (pGT432), medium expression (pGT433), low burden (pGT434) and high burden (pGT435). Each construct was individually assembled using Start-Stop Assembly in the destination vector pGT270 (Supplementary Figure S10). pGT434 was not cloneable in E. coli (in three independent attempts). Synechocystis was individually transformed with each pathway and PCR screening was used to assess genetic stability (detail in Supplementary Figure S11). In each case flanking sequences allowing integration at the ndhB neutral site in the Synechocystis genome were present and antibiotic selection pressure maintained the kanamycin resistance gene kanR, but gross deletions in the lycopene pathway-encoding constructs were observed. Promoters in descending order of strength as characterised using EYFP: P1 = SPLc25, P2 = SPLc19, P3 = SPLc47, P4 = SPLc3, P5 = SPLc45 and P6 = SPLc17. RBSs in descending order of strength as characterised using EYFP: R1 = RBSc4, R2 = RBSc21, R3 = RBSc110, R4 = RBSc123, R5 = RBSc48 and R6 = RBSc249.
