Figure 4.
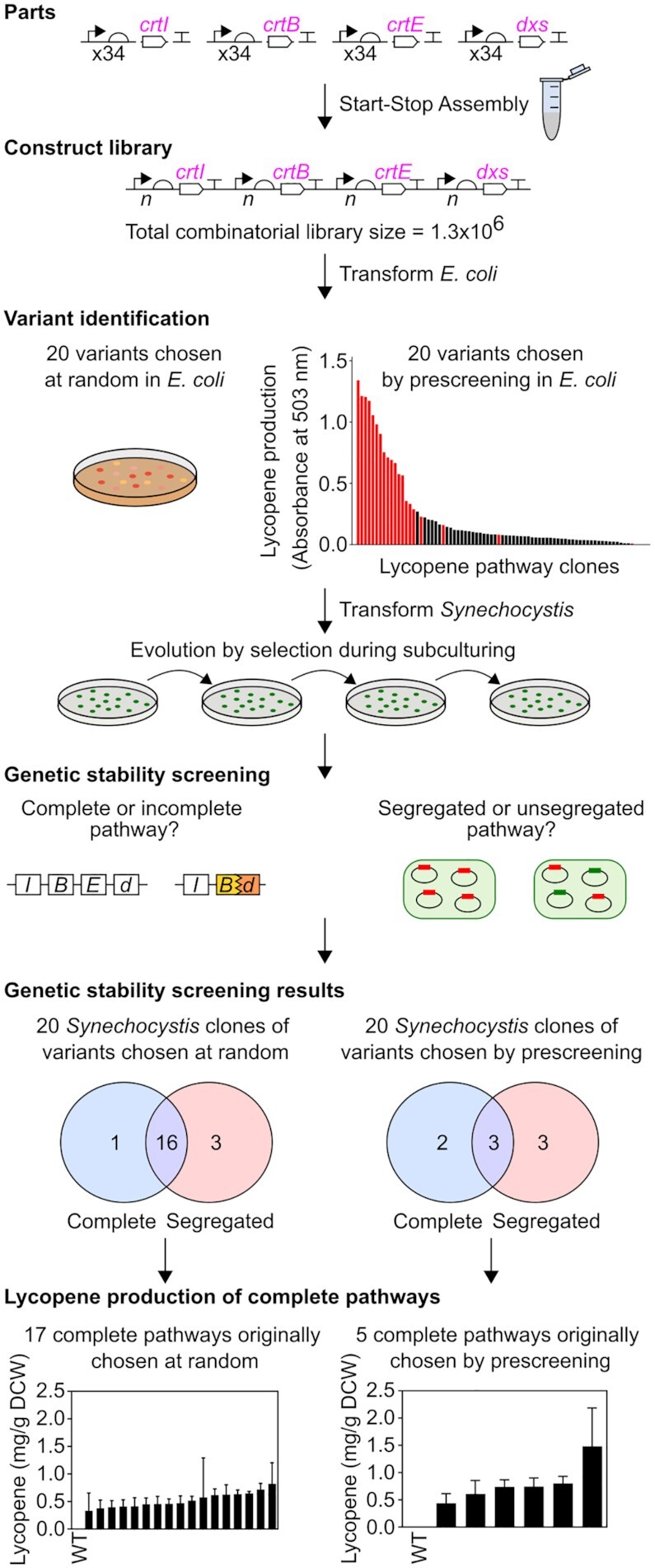
Genetic design, selection and evaluation of combinatorial lycopene pathway library. A library of lycopene pathway construct variants was assembled using Start-Stop Assembly in the destination vector pGT270. For combinatorial assembly equimolar mixtures of 34 composite promoter-RBS parts labelled ‘x34’ were used in Level 1 assemblies (Supplementary Figure S12). The uncertain representation of each promoter and RBS at each position following assembly is represented by ‘n’. The maximum library size was 344 = 1.3 × 106. E. coli was transformed with the combinatorial library and pathway clones were either chosen at random or after prescreening in E. coli (see text). Synechocystis was transformed with the chosen pathway variants, after which PCR screening was used to assess the completeness and segregation of the resultant clones (PCR screening details shown in Supplementary Figure S11). Synechocystis clones containing complete pathway constructs were grown in photoautotrophic batch cultures with constant light for two weeks, then lycopene accumulation was measured (detail in Supplementary Figure S15). Lycopene concentration was determined as mg lycopene per g dry cell weight (DCW). Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent biological replicates.
