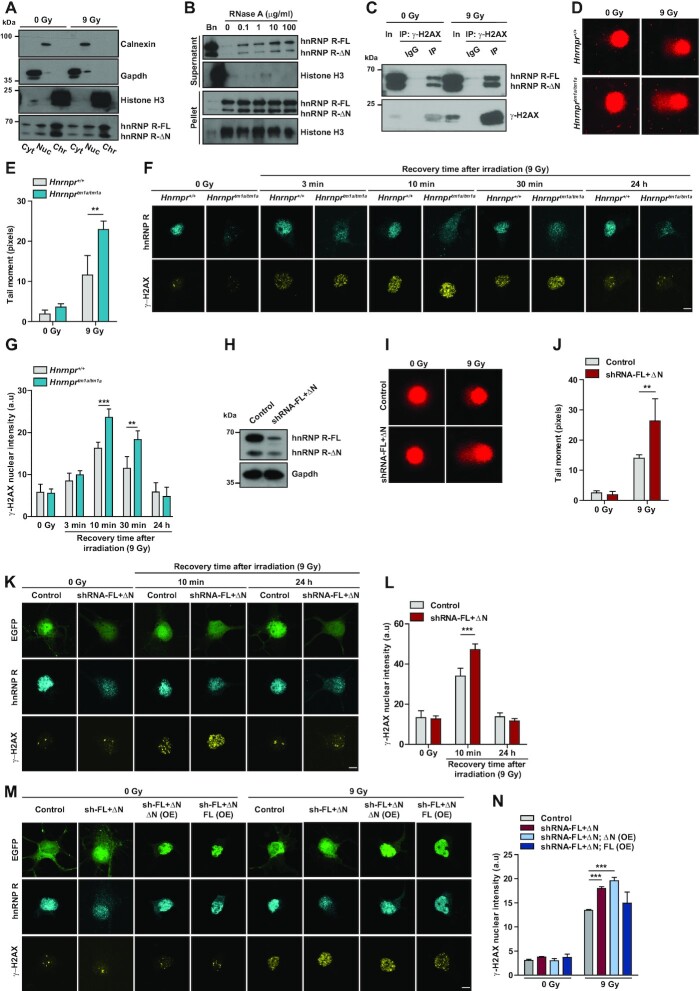
Figure 5.
Increased DNA damage and impaired DDR in Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a motoneurons. (A) Western blot analysis of subcellular fractions from control motoneurons (0 Gy) or motoneurons subjected to γ-irradiation (9 Gy). Motoneurons were fractioned into cytosolic (Cyt), nuclear soluble (Nuc) and chromatin-bound (Chr) fractions. Fractions were probed with the indicated antibodies. (B) Western blot analysis of chromatin fractions of NSC-34 cells incubated with Benzonase (Bn) or the indicated amounts of RNase A and separated into supernatant and pellet by centrifugation. (C) Immunoprecipitation of γ-H2AX from nuclear fractions of control (0 Gy) or irradiated (9 Gy) NSC-34 cells. Proteins were analyzed by western blot using antibodies against γ-H2AX or hnRNP R. In, input; IP, immunoprecipitation. (D) Representative images of alkaline comet assays performed on Hnrnpr+/+ and Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a motoneurons cultured for 6 DIV under control conditions (0 Gy) and after exposure to γ-irradiation (9 Gy). (E) Quantification of comet mean tail moments. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments; N = 71 nuclei for Hnrnpr+/+ (0 Gy), N = 55 nuclei for Hnrnpr+/+ (9 Gy), N = 82 nuclei for Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a (0 Gy) and N = 76 nuclei for Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a (9 Gy)). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test; **P ≤ 0.01. (F) Representative images of γ-H2AX immunofluorescence staining of Hnrnpr+/+ and Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a motoneurons under non-irradiated conditions (0 Gy) or after exposure to γ-irradiation (9 Gy) followed by the indicated recovery time. Scale bar: 5 μm. (G) Quantification of nuclear γ-H2AX immunostaining shown in (F). Data are mean ± SD (n = 4 independent experiments; N = 38 nuclei for Hnrnpr+/+ (0 Gy), N = 40 nuclei for Hnrnpr+/+ (9 Gy, 3 min recovery), N = 40 nuclei for Hnrnpr+/+ (9 Gy, 10 min recovery), N = 41 nuclei for Hnrnpr+/+ (9 Gy, 30 min recovery), N = 40 nuclei for Hnrnpr+/+ (9 Gy, 24 h recovery), N = 42 nuclei for Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a (0 Gy), N = 39 nuclei for Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a (9 Gy, 3 min recovery), N = 41 nuclei for Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a (9 Gy, 10 min recovery), N = 40 nuclei for Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a (9 Gy, 30 min recovery) and N = 39 nuclei for Hnrnprtm1a/tm1a (9 Gy, 24 h recovery)). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test; **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. (H) Western blot analysis of hnRNP R levels in cultured motoneurons transduced with control or shRNA against both hnRNP R isoforms (shRNA-FL+ΔN). Gapdh was used as loading control. (I) Representative images of alkaline comet assay performed on motoneurons transduced with control and shRNA-FL+ΔN under non-irradiated conditions (0 Gy) or after exposure to γ-irradiation (9 Gy). (J) Quantification of comet mean tail moments. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments; N = 32 nuclei for Control (0 Gy), N = 29 nuclei for Control (9 Gy), N = 37 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN (0 Gy) and N = 30 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN (0 Gy)). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test; **P ≤ 0.01. (K) Representative images of γ-H2AX immunofluorescence staining of control and shRNA-FL+ΔN-transduced motoneurons under non-irradiated conditions (0 Gy) or after exposure to γ-irradiation (9 Gy) followed by the indicated recovery time. EGFP was used as a marker to identify transduced cells. Scale bar: 5 μm. (L) Quantification of nuclear γ-H2AX immunostaining in (K). Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments; N = 34 nuclei for control (0 Gy), N = 32 nuclei for control (9 Gy, 10 min recovery), N = 22 nuclei for control (9 Gy, 24 h recovery), N = 21 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN (0 Gy), N = 33 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN (9 Gy, 10 min recovery), N = 36 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN (9 Gy, 24 h recovery)). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test; ***P ≤ 0.001. (M) Representative images of γ-H2AX immunofluorescence staining of motoneurons transduced with control, shRNA-FL+ΔN, shRNA-FL+ΔN; ΔN(OE) or shRNA-FL+ΔN; FL(OE) constructs under non-irradiated conditions (0 Gy) or after exposure to γ-irradiation (9 Gy) followed by 10 min recovery. EGFP was used as a marker to identify cells transduced with the control or shRNA-FL+ΔN construct. The rescue constructs shRNA-FL+ΔN; ΔN(OE) and shRNA-FL+ΔN; FL(OE) expressed EGFP-tagged hnRNP R-ΔN or hnRNP R-FL, respectively, in addition to an shRNA targeting both endogenous hnRNP R isoforms. Scale bar: 5 μm. (N) Quantification of nuclear γ-H2AX immunostaining in (M). Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments; N = 25 nuclei for control (0 Gy), N = 25 nuclei for control (9 Gy), N = 25 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN (0 Gy), N = 25 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN (9 Gy), N = 25 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN; ΔN(OE) (0 Gy), N = 25 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN; ΔN(OE) (9 Gy), N = 25 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN; FL(OE) (0 Gy) and N = 25 nuclei for shRNA-FL+ΔN; FL(OE) (9 Gy)). Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test; ***P ≤ 0.001.