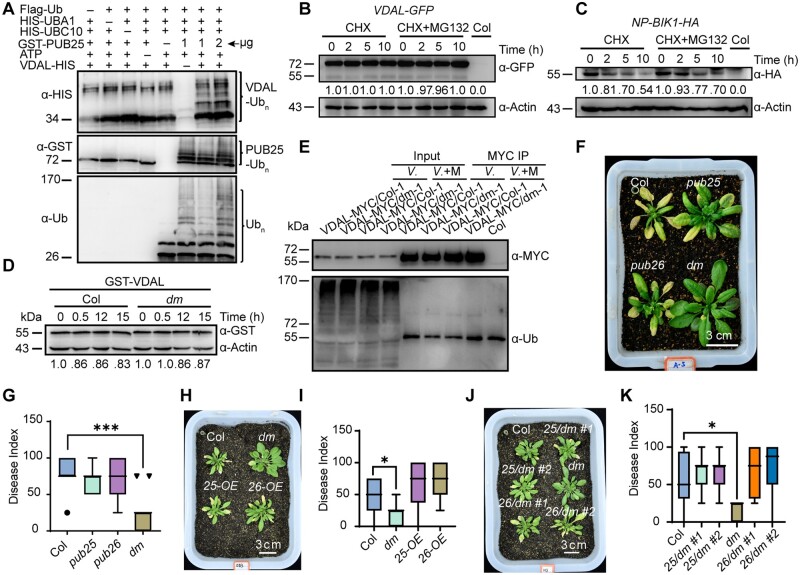
Figure 3.
VDAL is a putative substrate of PUB25 in vitro, and PUB25 and PUB26 negatively regulate plant resistance to Verticillium wilt. A, PUB25 ubiquitination of VDAL in vitro. Different ubiquitination reaction systems with 40 mM ATP from different proteins purified from E. coli were incubated at 30°C for 3 h. The VDAL ubiquitination and PUB25 ubiquitination were detected by anti-HIS and anti-GST antibodies, respectively. The total ubiquitination signal was detected with anti-Ub antibodies. The numbers indicate the amount of GST-PUB25 added in the reaction. B, Degradation pattern of VDAL in the presence of CHX with or without MG132. The 12-day-old VDAL-GFP seedlings were treated with CHX or CHX with MG132 for different times. Total proteins were extracted. Immunoblotting analysis was carried out with anti-GFP antibodies. Actin was an equal loading control. The relative protein level was quantified with ImageJ. C, Degradation pattern of BIK1 in the presence of CHX with or without MG132. The 12-day-old BIK1-HA seedlings were treated with CHX or CHX with MG132 for different times. Total proteins were extracted. Immunoblotting analysis was carried out with anti-HA antibodies. Actin was an equal loading control. The relative protein level was quantified with ImageJ. D, VDAL degradation in Col and pub25 pub26 dm. Total proteins extracted from 12-day-old pub25 pub26 and Col seedlings were incubated with equal GST-VDAL at 25°C for different time. Immunoblotting analysis was carried out with anti-GST antibodies. Actin was an equal loading control. The relative protein level was quantified with ImageJ. E, Assessment of VDAL ubiquitination in planta. The 12-day-old VDAL-MYC seedlings were treated with V. dahliae or V. dahliae combined MG132 for 12 h. Total extracted proteins were immunoprecipitated with beads coated with anti-MYC antibodies. Immunoblotting analysis was carried out with anti-MYC and anti-Ub antibodies. F, pub25 pub26 dm resistance to Verticillium wilt compared with the wild-type or pub25 and pub26 single mutant. The plants grown in the greenhouse for 2 weeks were dipped into the V. dahliae spore suspension for 5 min. Photos were taken at 20 dpi. G, Statistical analysis of the disease index of Col, pub25, pub26 and pub25 pub26 dm in F, count with at least 15 plants. H, Comparison of PUB25 and PUB26 overexpression transgenic line susceptibility to Verticillium wilt caused by V. dahliae with that of the wild-type. The plants grown in the greenhouse for 2 weeks were dipped into the V. dahliae spore suspension for 5 min. Photos were taken at 15 dpi. I, Statistical analysis of the disease index of PUB25-OE, PUB26-OE, dm, and Col in (H), count with at least 15 plants. J, Comparison of PUB25 and PUB26 transgenic complementation lines with Col during Verticillium wilt caused by V. dahliae. The plants grown in the greenhouse for 2 weeks were dipped into the V. dahliae spore suspension for 5 min. Photos were taken at 20 dpi. K, Statistical analysis of the disease index of plants indicated in (J), count with at least 15 plants. *, **, and *** in (G), (I), and (K) represent significant difference (P < 0.05), and extremely significant difference (P < 0.001), respectively, one-way ANOVA. The experiments were repeated independently three times with similar results.