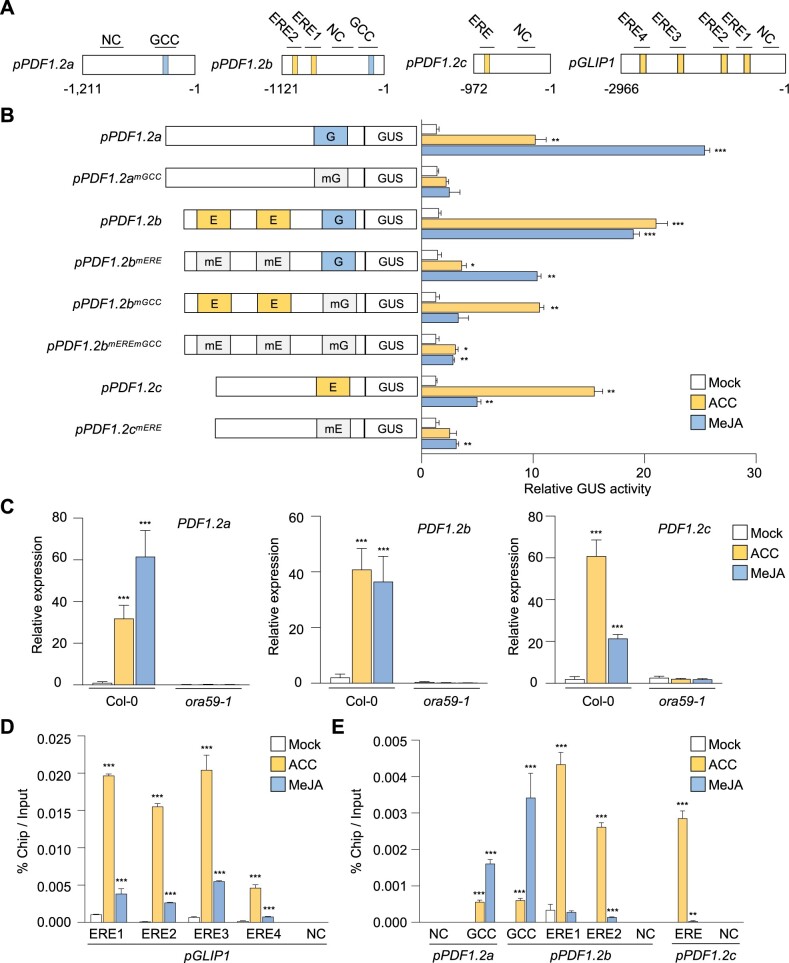
Figure 4.
ORA59 directly binds to ERE and GCC box of GLIP1 and PDF1.2 promoters in ACC- and JA-dependent manners. A, Schematic diagram of the ERE and GCC box elements in PDF1.2 and GLIP1 promoters. B, GUS reporter assays showing the ACC- and MeJA-induced expression of the GUS reporter gene driven by native or ERE/GCC box-mutated PDF1.2a, b, and c promoters. The left panel illustrates ERE and GCC box mutations of PDF1.2a, b, and c promoters. E, ERE; G, GCC box; mE, mutated ERE; mG, mutated GCC box. Transfected protoplasts were treated with mock (water), ACC (200 μM), and MeJA (20 µM) for 6 h. C, Analysis of PDF1.2a, b, and c expression in ACC- and MeJA-treated plants. D and E, ChIP-qPCR analysis for in vivo binding of ORA59 to ERE and GCC box sequences in the GLIP1 (D) and PDF1.2 (E) promoters. Chromatins from ACC- and MeJA-treated 35S:ORA59-GFP leaves were immunoprecipitated with an anti-GFP antibody. The enrichment of target element sequences is displayed as the percentage of input DNA. In (C–E), six-week-old plants were treated with ACC (1 mM) and MeJA (100 µM) for 6 h. NC indicates the negative control region without ERE and GCC box sequences. Values represent means ± sd (n = 3 biological replicates). Asterisks indicate significant differences from mock treatment as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).