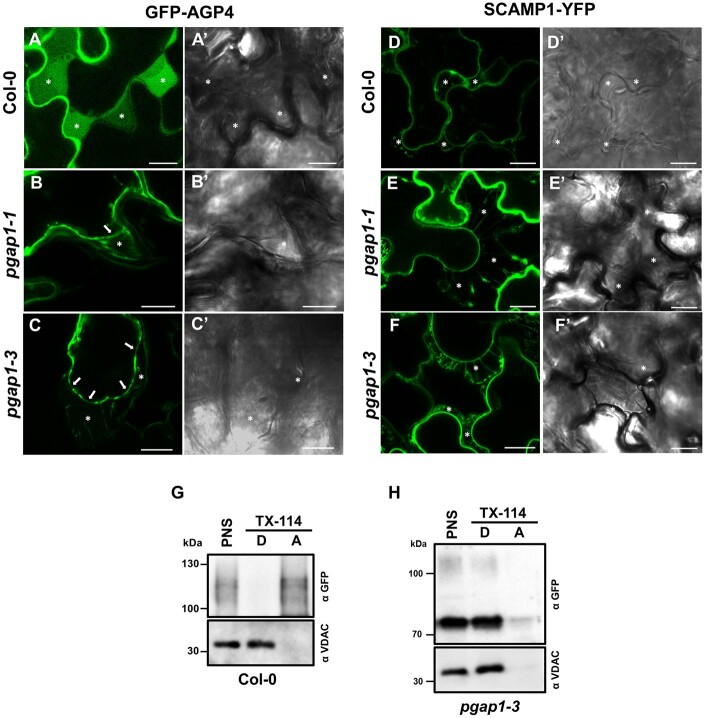
Figure 10.
Localization of plasma membrane proteins following plasmolysis. A–F, Transient expression experiments in wild-type (Col-0), pgap1–1 and pgap1–3 Arabidopsis seedlings. Left panels (A–F) show CLSM images; right panels (A′–F′) show phase-contrast images. GFP-AGP4, a GPI-AP, mainly localized to the apoplast in wild-type seedlings (A), as shown after plasmolysis following 750 mM mannitol treatment (see asterisks). In the pgap1–1 (B) and pgap1–3 (C) mutants, GFP-AGP4 mainly localized to the ER, but the small fraction of GFP-AGP4 reaching the cell surface remained at the plasma membrane (see arrows) and was not released to the apoplast (asterisks). Note the Hechtian strands in the apoplast of pgap1 mutants. SCAMP1-YFP, a transmembrane plasma membrane protein, showed characteristic plasma membrane localization in a plasmolized cell in wild-type (D) and in pgap1–1 (E) and pgap1–3 (F) mutants. Note the Hechtian strands in the apoplast in all cases. G–H, PNSs from wild-type (G) and pgap1–3 (H) Arabidopsis cotyledons transiently expressing GFP-AGP4 were treated with Triton X-114, and detergent (D) and aqueous (A) phases were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting with GFP antibodies (to detect GFP-AGP4). In wild-type seedlings, GFP-AGP4 mainly appears in the aqueous phase, consistent to its apoplast localization (G). In contrast, GFP-AGP4 appears in the detergent phase, as the membrane marker VDAC, in the pgap1–3 mutant (H). Scale bars = 10 µm.