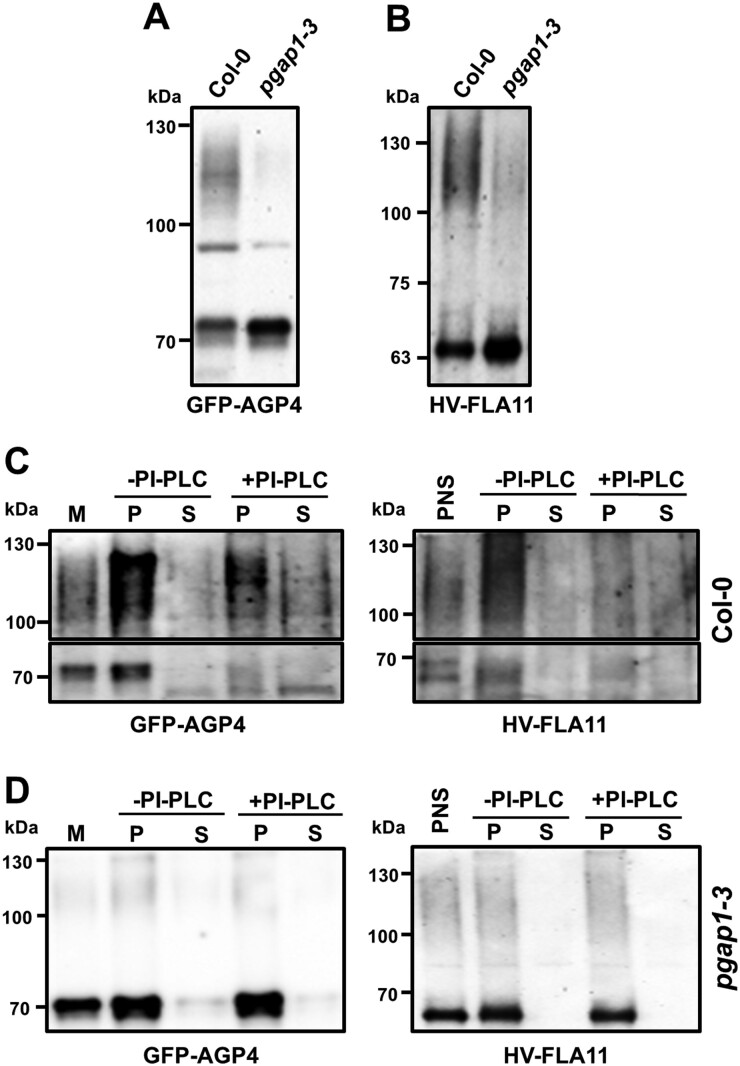
Figure 9.
Biochemical characterization of GFP-AGP4 and V-FLA11 in wild-type and pgap1–3 seedlings. A, B, PNS were obtained from cotyledons of wild-type (Col) and pgap1–3 mutant seedlings transiently expressing GFP-AGP4 (A) and V-FLA11 (B) and analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against GFP (to detect GFP-AGP4 and V-FLA11). In wild-type seedlings, both GFP-AGP4 and V-FLA11 showed a smear with a molecular mass around 100–130 kDa, which correspond to the plasma membrane form of GFP-AGP4 (Bernat-Silvestre, 2021) and V-FLA11 (Supplemental Figure S12), and additional bands (around 70 kDa and 63 kDa) corresponding to the ER forms of GFP-GP4 (Bernat-Silvestre et al., 2020) and V-FLA11 (Supplemental Figure S12), respectively. In the pgap1–3 mutant, there was a strong decrease in the smear form (plasma membrane) of both proteins with a concomitant increase in their ER forms. C, D, Left (GFP-AGP4). Membrane fractions were obtained from PNSs of wild-type (C) or pgap1–3 mutant (D) seedlings expressing GFP-AGP4 and incubated in the absence or presence of PI-PLC. Then, membranes were pelleted by centrifugation and pellets (P) and supernatants (S) were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against GFP to detect GFP-AGP4. Right (V-FLA11). PI-PLC treatment was performed directly in the PNSs, membranes were also pelleted by centrifugation and pellets and supernatants analyzed as before. In C, the upper part of the immunoblotting shows the smear form of GFP-AGP4 (left) or V-FLA11 (right) while the lower part highlights the ER bands of GFP-AGP4 (left) or V-FLA11 (right). Notice the decrease of both the smear forms and the lower ER bands from the pellet fraction and their partial appearance in the supernatant in wild-type seedlings. The presence of both forms in the supernatant seems to be only partial, probably due to degradation upon release from the membranes. In contrast, both forms are PI-PLC resistant in the pgap1–3 mutant.