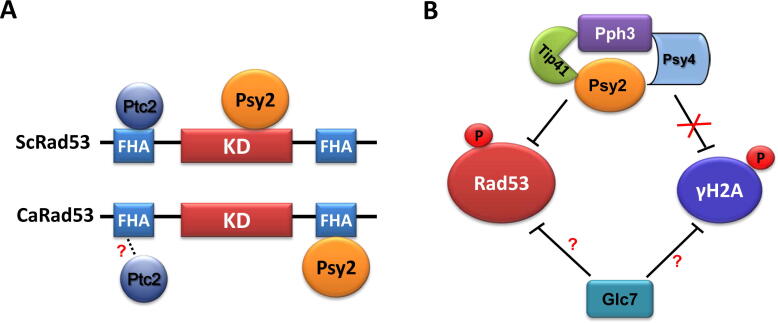
Fig. 2.
Phosphatases involved in the dephosphorylation of checkpoint kinase Rad53. (A) In S. cerevisiae, ScPsy2 and ScPtc2 are required for the dephosphorylation of ScRad53; ScPsy2 interacts with the kinase domain (KD) and ScPtc2 interacts with the FHA (N terminus) domain. In C. albicans, Psy2 interacts with the FHA (C terminus) domain, but Ptc2 shows no clear interaction with Rad53. (B) Pph3 and Psy2 form a complex and play a dominant role in the dephosphorylation of Rad53 in C. albicans. Psy4 and Tip41 act as adaptors for Pph3 and Psy2. In particular, Tip41 plays an important role in the dephosphorylation of Rad53 during the recovery from DNA damage stress, while Psy4 seems dispensable for the dephosphorylation of Rad53. Unlike the pattern in S. cerevisiae, the Pph3-Psy2-Psy4 complex is not involved in the dephosphorylation of H2A. Additionally, Glc7 regulates the dephosphorylation of Rad53 both in S. cerevisiae and C. albicans, but the direct interaction between Rad53 and Glc7 is unclear. Moreover, Glc7 is involved in the dephosphorylation of γH2A in S. cerevisiae, but the role in C. albicans remains to be established. The red question mark means uncovered interaction according to current data. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)