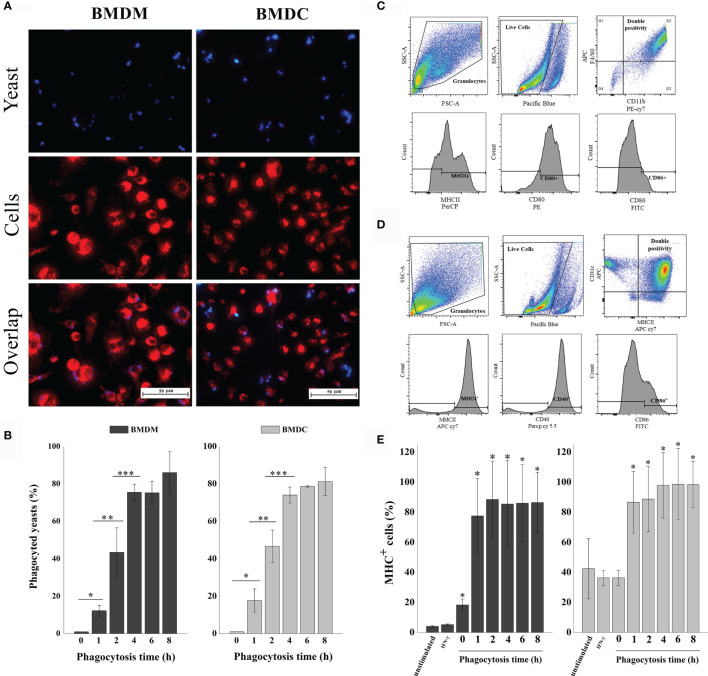
Figure 2.
Phagocytosis of H. capsulatum yeasts by murine BMDM and BMDCs. (A) Fluorescence microscopy of yeasts (blue) ingested by BMDM or BMDC (red). Overlap: Both images, with yeast and BMDM or BMDC, represent the same quadrant of the culture plate well according to the phagocytosis time determined of 4 hours. (B) Determination of the percentage of phagocyted cells. The percentage of cells ingested was determined by counting the samples stained with giemsa under a light microscope. *differ from zero time, **differ from one time, ***differ from two time by the Tukey’s test, p < 0.01. (C) Analysis strategy used for phenotyping and activation of BMDM. First, the cells were separated by granularity (SSC) and size (FSC), followed by live/dead- cell staining. Double positive cells for CD11b and F4/80 were classified as Mφ and analyzed for CD80, CD86 and MHC-II expression. (D) Analysis strategy used for phenotyping and activation of BMDCs. The cells were separated by granularity (SSC) and size (FSC), followed by live/dead- cell staining. Double positive cells for CD11c and MHC-II were classified as DCs and analyzed for CD40 and CD86 expression. (E) Percentage of MHC-II expression by BMDM or BMDC. Unstimulated cells, only stimulated with IFN-γ and phagocytosis times of 0, 1, 2, 4, 6 and 8 hours. Unmarked, dead, and unstimulated cells were used as biological controls. *Differ from unstimulated control by the Tukey’s test, p<0.01. These results are representative of the biological triplicate.