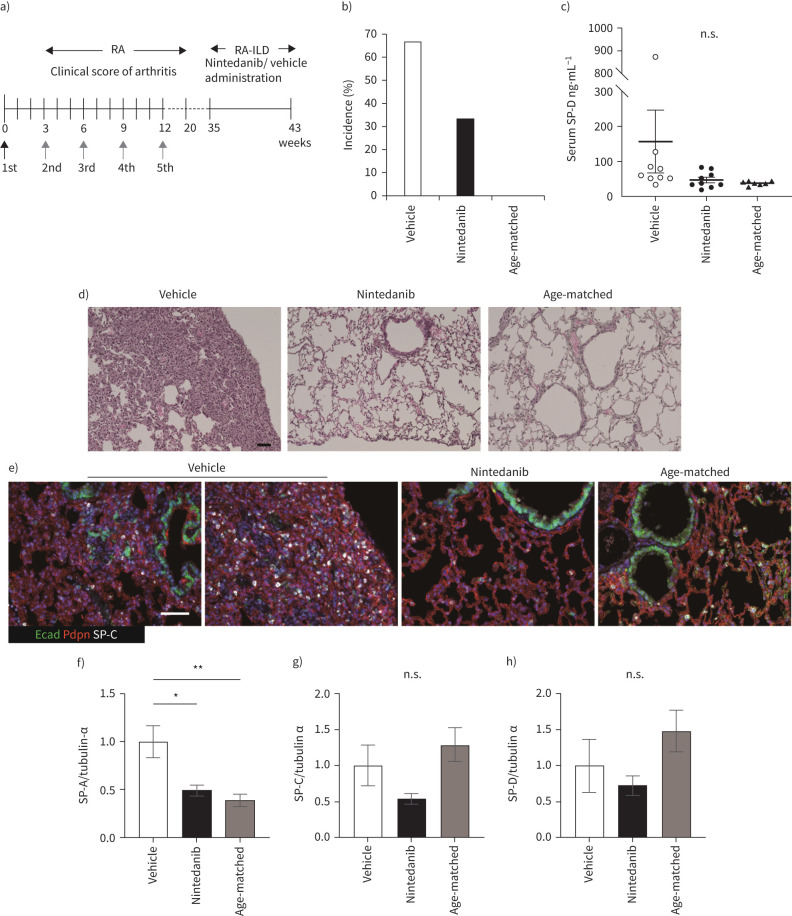
FIGURE 1.
Nintedanib attenuates development of interstitial lung disease (ILD) after inflammatory arthritis. a) The schematic diagram shows the time course of bovine Type II collagen (bColII) immunization and the oral administration of nintedanib, which is done daily for 2 months from 35 weeks after first immunization. Arrows indicate bColII immunization (black: bColII/complete Freund's adjuvant, grey: bColII/incomplete Freund's adjuvant). b) The incidence of ILD is determined by overall cut-off of serum SP-D (>53.9 ng·mL−1) at 43 weeks after the first immunization of bColII of nine mice in each group. c) Serum SP-D levels are measured at 43 weeks after first immunization of bColII. Data are presented as mean±SE of nine mice for each group (a–c). Each symbol represents vehicle (white circle), nintedanib (black circle) and age-matched control (black triangle), respectively. d) and e) Histopathology by haematoxylin–eosin (H&E) staining (d) and triple immunohistochemical staining for podoplanin (Pdpn, red), E-cadherin (Ecad, green) and SP-C (white) are performed in vehicle, nintedanib-treated or age-matched control mice (e). Scale bars=50 μm (black and white). f–h) The expression of SP-A (f), -C (g) and -D (h) in the lung tissue is assessed by Western blotting. Data are presented as mean±se of four mice for each group. *p<0.05; **p<0.001, compared with vehicle group. n.s., nonsignificant.