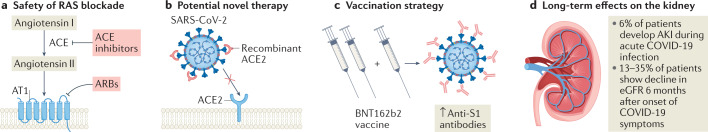
Fig. 1. New knowledge of COVID-19 and the kidneys in 2021.
a | Renin–angiotensin system (RAS) blockade with either angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) is not associated with increased risk or severity of COVID-19 in patients with kidney failure. b | Recombinant ACE2 protein could be a potential therapeutic agent to prevent or treat COVID-19. c | A third dose of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine increases anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 (anti-S1) antibodies in patients with kidney failure on dialysis. d | In addition to the development of acute kidney injury (AKI) during acute COVID-19, the disease can lead to loss of kidney function in the long term. AT1, angiotensin II receptor type 1; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.