Figure 3.
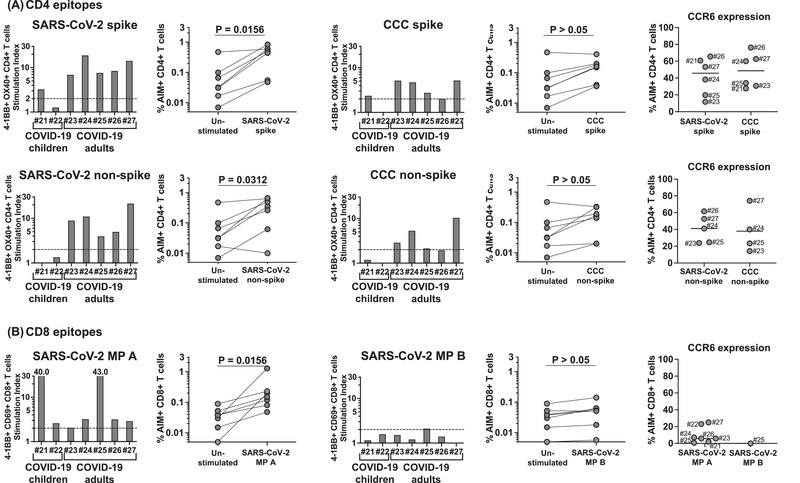
CD4+ and CD8+ T‐cell responses to SARS‐CoV‐2 and CCC peptide megapools in convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected children and adults. CD4+ and CD8+ T‐cell responses to SARS‐CoV‐2 and CCC were tested on two convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected children (#21‐22, 84 and 103 days after disease onset, respectively) and on five convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected adult subjects (#23–27, 100 to 146 days after disease onset). (A) CD4+ T‐cell responses and CCR6 expression to CD4 peptide megapools in each convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected subject. One convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected child (#21) and all five convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected adults (#23 ‐ 27) showed CD4+ T‐cells responses to the CD4 megapools derived from both SARS‐CoV‐2 and CCC. CCR6 expression on CD4+ T cells from convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2 infected subjects was similar to the MIS‐C subjects. (B) CD8+ T‐cell responses and CCR6 expression to CD8 peptide megapools in each convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected subject. Symbols represent the data derived from each individual subject. Seven subjects were studied in four independent experiments (one to three subjects/experiment depending upon enrollment). All the convalescent SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected subjects showed CD8+ T‐cell responses to at least one of the SARS‐CoV‐2 CD8 megapools. Low percentages of AIM+ CD8+ T cells expressed CCR6 as found in MIS‐C. Comparisons of the percentage of AIM+ T cells in the unstimulated control and peptide megapool‐stimulated cultures were tested by Wilcoxon signed rank test.
