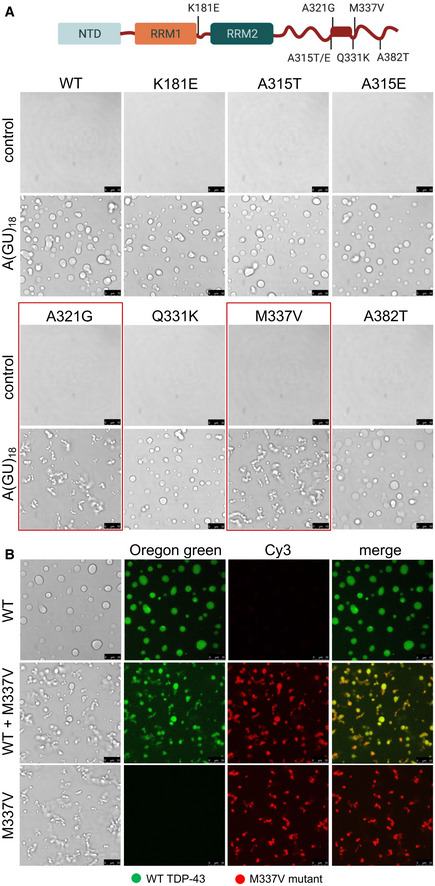
TDP‐43 ALS‐linked amino acid substitutions K181E, A315T/E, A321G, Q331K, M337V, and A382T. Boxed in the C‐terminal domain is the α‐helical structure within the conserved region (a.a. 320–343). Droplets formed by TDP‐43 wild‐type (WT) and the different mutants (4 μM) observed by brightfield microscopy in the presence of no RNA control or A(GU)18 RNA (3.9 μM) at 250 mM of NaCl. Mutations A321G and M337V, showing decreased liquidity of the condensates in the presence of A(GU)18, are boxed in red. Representative images for three biological replicates using three different protein preparations of WT and M337V, 2 preparations of A321G, Q331K, K181E and one preparation of A315T/E and A382T. Scale bars, 10 μm.