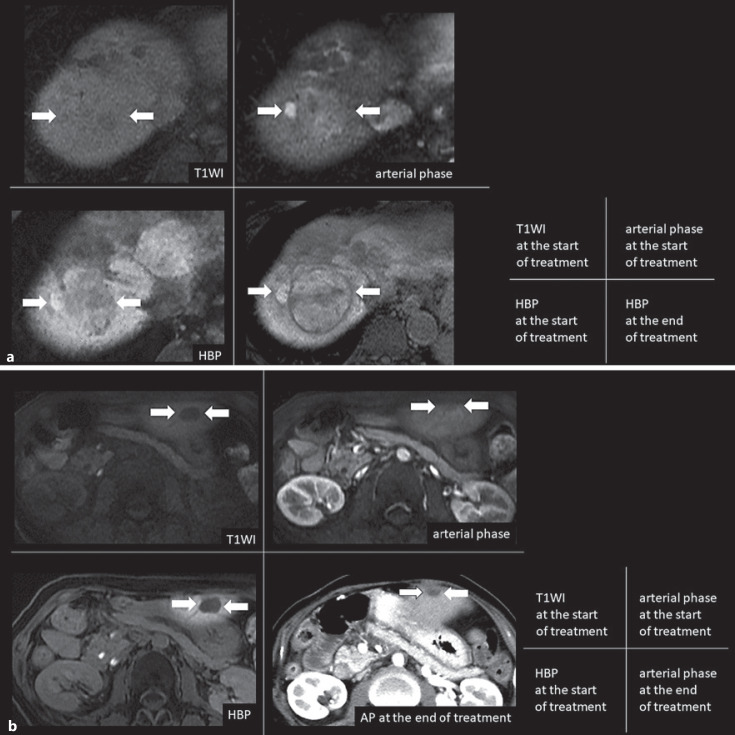
Fig. 5.
a Typical treatment outcome in higher enhancement HCC nodule with tumor growth 60s male with Child-Pugh score 5, HCV positive (post-SVR) with alcohol intake. The average RER of the 2 readers was 1.044 in the large intrahepatic nodule of segment 8. After discontinuing sorafenib as the 1st line, anti-PD-L1 monotherapy was started as the 2nd line therapy, and the nodule of segment 8 increased from 40 mm to 58 mm in 1.57 months, resulting in PD. b A typical treatment outcome in hypointense HCC nodule with tumor reduction 50s female with Child-Pugh score 5, HCV and HBV negative patient. The average RER of the 2 readers was 0.703 in the small intrahepatic nodule of segment 2. After discontinuing sorafenib as the 1st line, anti-PD-1 monotherapy was started as the 2nd line therapy, and the nodule of segment 2 decreased from 14 mm to 5 mm in 4 months, resulting in PR. RER, relative enhancement ratio; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HBV, hepatitis B virus; SVR, sustained virological response; RIR, the relative intensity ratio; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response; HBP, hepatobiliary phase; T1WI, T1-weighted image; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1.