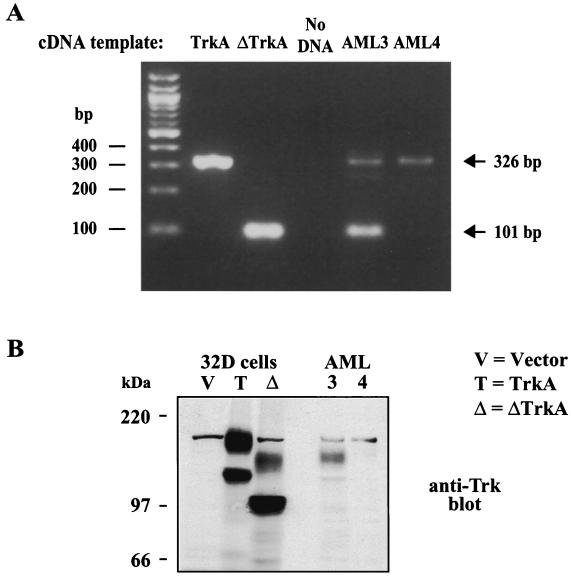
FIG. 9.
ΔTrkA was expressed in the AML patient. (A) Primers were designed based on the ΔTrkA cDNA sequence in order to discriminate between wild-type TrkA and ΔTrkA. These primers were used to PCR amplify TrkA cDNA, ΔTrkA cDNA, AML3 library cDNA (the library screened in this study), and AML4 library cDNA (an unrelated AML patient sample). The 326-bp PCR fragment indicates the presence of the wild-type TrkA cDNA, while the 101-bp PCR product indicates the presence of the ΔTrkA cDNA. (B) Total cell lysates of 32D cells expressing vector, TrkA, ΔTrkA, and protein extracts from the AML3 patient and the unrelated AML4 patient were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Trk antibodies.