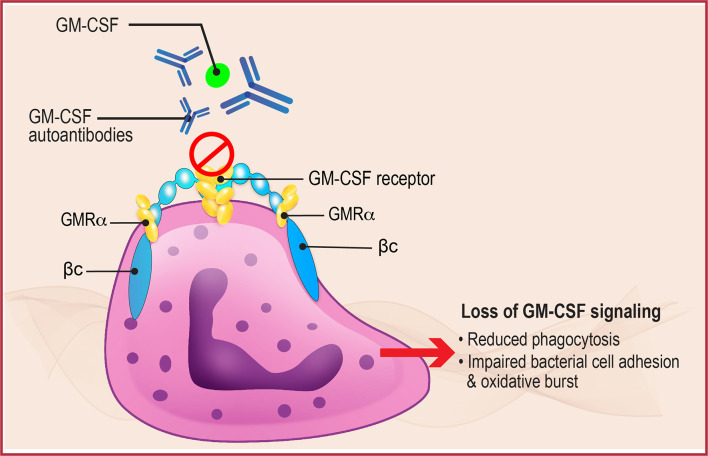
Figure 2.
Neutrophil Dysregulation in aPAP. GM-CSF normally binds to the GM-CSF receptor, present on the surface of neutrophils (shown here) and alveolar macrophages, to initiate downstream signaling that regulates multiple functions including phagocytosis, bacterial cell adhesion, and oxidative burst. In aPAP, high levels of GM-CSF autoantibodies bind to GM-CSF preventing binding and receptor activation, thus inhibiting receptor signaling and leading to neutrophil and macrophage dysfunction. βc, GM-CSF receptor common β-subunit; GMRα, GM-CSF receptor subunit-α.