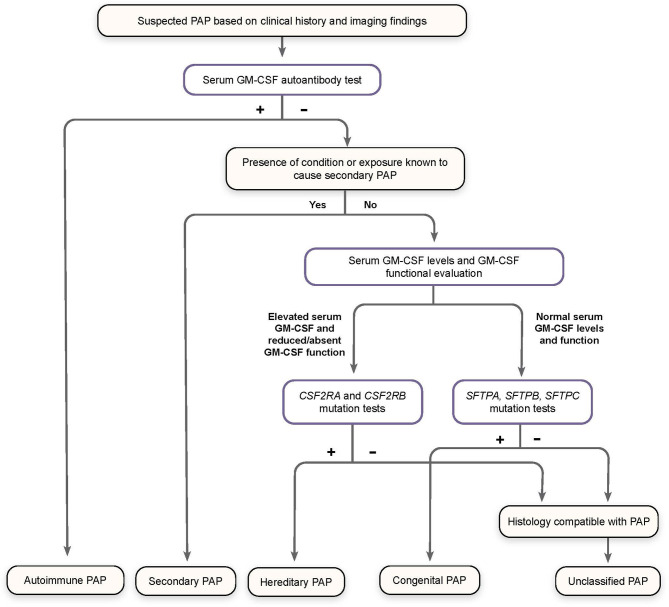
Figure 3.
Algorithm for Diagnosis of Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (PAP). Patients suspected of having PAP on the basis of clinical history and imaging findings should undergo screening for serum GM-CSF autoantibodies. Elevated autoantibody levels confirm a diagnosis of autoimmune PAP. Patients with a known condition or exposure associated with secondary PAP who do not have increased GM-CSF autoantibodies are diagnosed accordingly. Otherwise, patients should be screened for serum GM-CSF levels and GM-CSF function signaling by flow cytometry, as well as genomic analysis for mutations affecting GM-CSF receptor genes (CSF2RA and CSF2RB) and those related to surfactant production (SFTPA, SFTPB, SFTPC), to confirm a diagnosis of hereditary, congenital, or unclassified PAP, all of which are exceedingly rare. (Adapted from “Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis,” by BC Trapnell, 2019, Nat Rev Dis Primers, 5:16:8.).