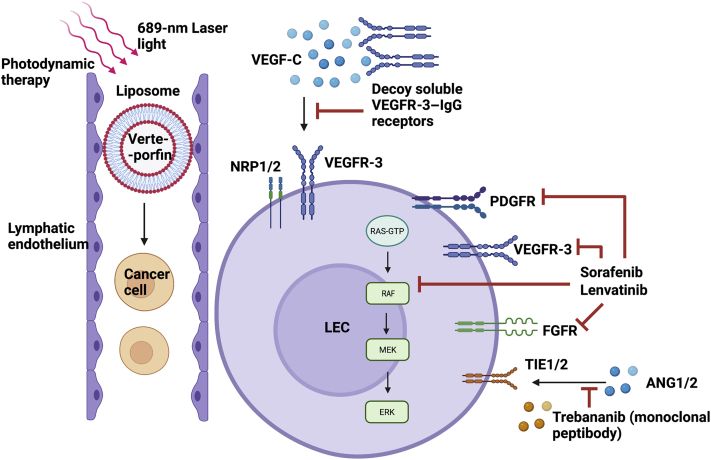
Figure 2.
Current therapeutic and treatment modalities targeting tumor lymphangiogenesis. Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-3 receptors serve as decoy agents that bind and inhibit soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, thus keeping them away from VEGFR-3 or neuropilin-1/2 (NRP1/2) coreceptor on lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) surface. Multikinase inhibitors, like sorafenib and lenvatinib, bind to and block multiple receptors (which bind to lymphangiogenic factors), such as platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), VEGFR-3, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), and rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF) kinases. Monoclonal peptibodies, like trebananib, bind to tyrosine kinase with Ig-like and epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains 1/2 (TIE1/2) receptor, thus preventing binding of angiopoietin-1/2 (ANG1/2). Photodynamic therapy takes place through liposome-mediated, lymphatic-specific delivery of verteporfin, which can kill cancer cells inside lymphatic vessels (LVs), thus reducing cancer metastasis. This specifically happens only inside the LVs. MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; RAS, rat sarcoma. Generated with BioRender.com (Toronto, ON, Canada).