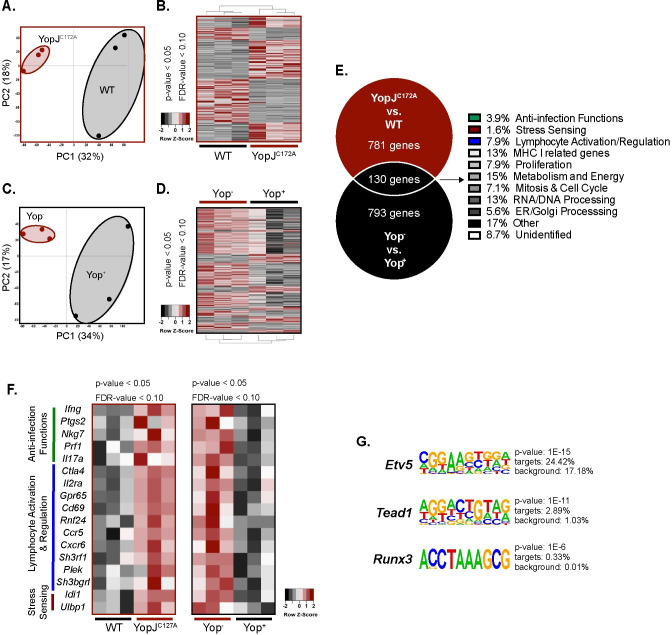
Fig 4. YopJ translocation leads to the inhibition of a broad anti-microbial gene response from Vγ4 T cells.
(A and B) MLN suspensions from L. monocytogenes infected mice were stimulated with 10 MOI of WT or YopJC172A Y. pseudotuberculosis for 24 hours. Antibiotics were given 2 hours post-stimulation. Five hundred Vγ1.1/2- CD44hi CD27- γδ T cells from each stimulation were flow sorted and processed for RNA sequencing. (A) PCA plots are depicted for similarity of groups YopJC172A and WT Y. pseudotuberculosis stimulated Vγ1.1/2- CD44hi CD27- γδ T cells. (B) Heat maps are depicted for differentially expressed genes of YopJC172A or WT Y. pseudotuberculosis stimulated Vγ1.1/2- CD44hi CD27- γδ T cells. (C and D) MLN suspension from L. monocytogenes infected mice were stimulated with 1 MOI of WT Yptb-βla. Five hundred Yop+ or Yop- Vγ1.1/2- CD44hi CD27- γδ T cells were flow sorted and processed for RNA sequencing. (C) PCA plots are depicted for similarity of Yop+ or Yop- Vγ1.1/2- CD44hi CD27- γδ T cells. (D) Heat maps are depicted for differentially expressed genes of Yop- or Yop+ stimulated Vγ1.1/2- CD44hi CD27- γδ T cells. (E-G) A Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes (higher) that overlapped between RNA sequencing analyses favoring YopJC172A Y. pseudotuberculosis stimulation or Yop- cells is displayed. Shared genes were categorized by gene function. (F) The heat map highlights differentially expressed genes among Vγ1.1/2- CD44hi CD27- γδ T cells from the indicated stimulations and categories. (G) Homer motif analysis was performed on the RNA sequencing dataset. Motifs and associated genes to YopJC172A stimulated Vγ1.1/2- CD44hi CD27- γδ T cells are highlighted. Each experiment was performed with 3 biologic samples per group. Cutoffs for significant genes are p < 0.05 and FDR < 0.10.