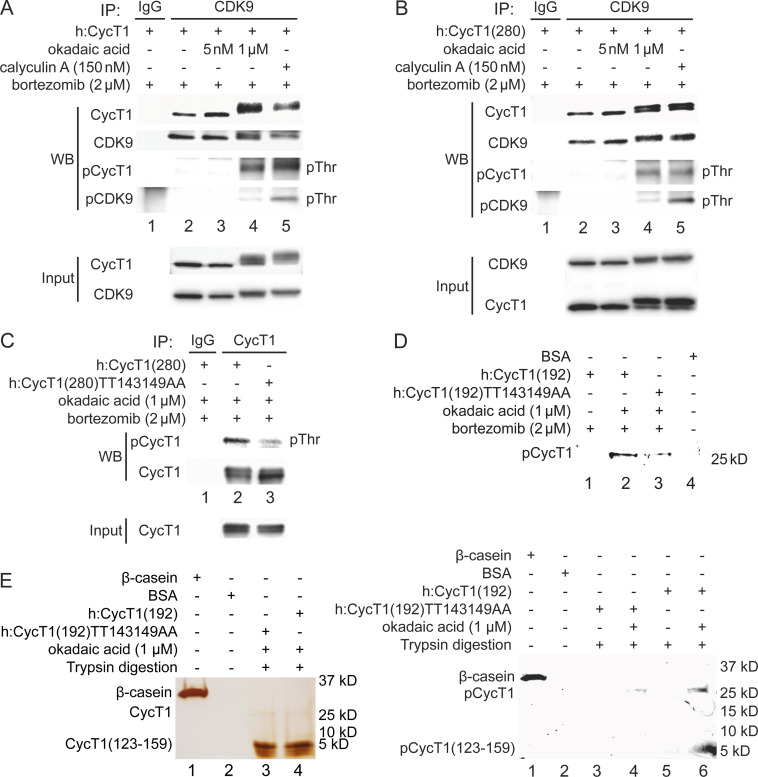
Figure 2. Phosphorylation of Thr143 and Thr149 in CycT1 contributes to its binding to CDK9.
(A) Threonine phosphorylation is detected in the full-length CycT1 protein. CycT1 was expressed in 293T cells untreated or treated with 5 nM or 1 μM okadaic acid, or 150 nM calyculin A (+/- signs on top). Co-IPs with CDK9 were then probed with anti-HA and anti-CDK9 antibodies in panels 1 and 2, with anti-phospho-threonine (pThr) antibodies in panels 3 and 4. Panels 5 and 6 contain input levels of CycT1 and CDK9 proteins. (B) Threonine phosphorylation is detected in CycT1(280). CycT1(280) protein was expressed in 293T cells untreated or treated with 5 nM or 1 μM okadaic acid, or 150 nM calyculin A (+/- signs on top). Co-IPs with CDK9 were then probed with anti-HA and anti-CDK9 antibodies in panels 1 and 2, with anti-pThr antibodies in panels 3 and 4. Panels 5 and 6 contain input levels of CycT1 and CDK9 proteins. (C) Thr143 and Thr149 are major phospho-threonine residues in CycT1(280). WT CycT1(280) or mutant CycT1(280)TT143149AA proteins were expressed in the presence of bortezomib and 1 μM okadaic acid in 293T cells. IPs with CycT1 were then probed with anti-pThr and anti-HA antibodies in panels 1 and 2. Panel 3 contains input levels of CycT1 proteins. (D) Thr143 and Thr149 are major phosphorylated residues in CycT1(192). WT CycT1(192) or mutant CycT1(192)TT143149AA proteins were expressed in the presence of bortezomib and/or 1 μM okadaic acid (+/- signs on top) in 293T cells. After IPs with anti-HA antibodies, IPed samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE, then phosphorylated proteins were detected by in-gel Phospho-Tag staining, with unphosphorylated BSA protein as the negative control. (E) Direct detection of Thr143/Thr149 phosphorylation by phosphopeptide mapping analysis. WT CycT1(192) or mutant CycT1(192)TT143149AA proteins were expressed in the presence of bortezomib and/or 1 μM okadaic acid (+/- signs on top) in 293T cells. After IP with anti-HA antibodies. IPed samples were digested by trypsin and subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by silver staining (left panel) in-gel Phospho-Tag staining (right panel), using phosphorylated β-casein protein as the positive control and unphosphorylated BSA protein as the negative control.
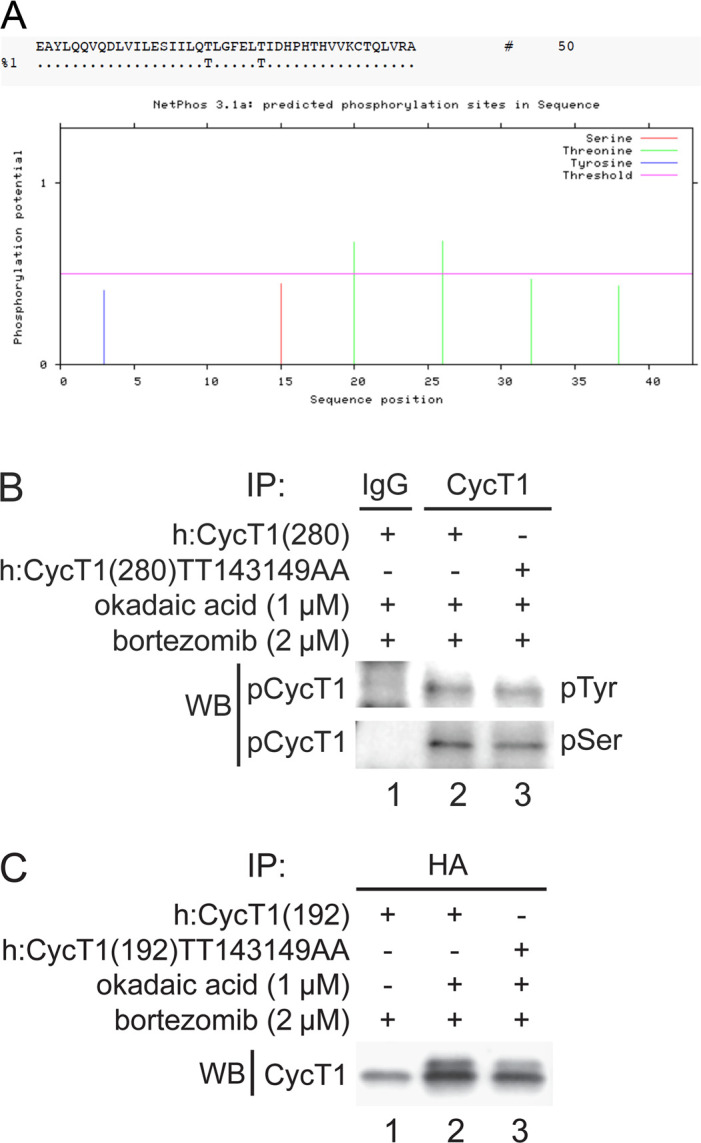
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Thr143 and Thr149 are main phosphorylation sites in CycT1.