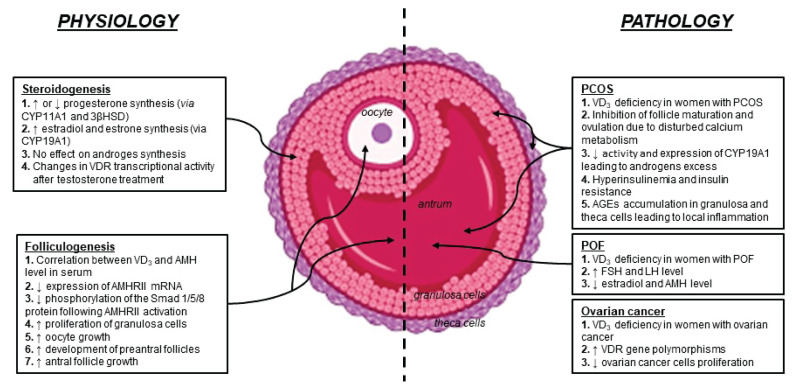
Fig. 1.
Vitamin D3 contribution to physiological and pathological processes within the ovary. AGEs: advanced glycation end-products; AMH: anti-Müllerian hormone; AMHRII: AMH receptor type II; 3β-HSD: 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; CYP11A1: cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme; CYP19A1: cytochrome P450 aromatase; FSH: follicle-stimulating hormone; GCs: granulosa cells; LH: luteinizing hormone; PCOS: polycystic ovary syndrome; POF: premature ovarian failure; TCs: theca cells; VD3: vitamin D3; VDR: vitamin D3 receptor.