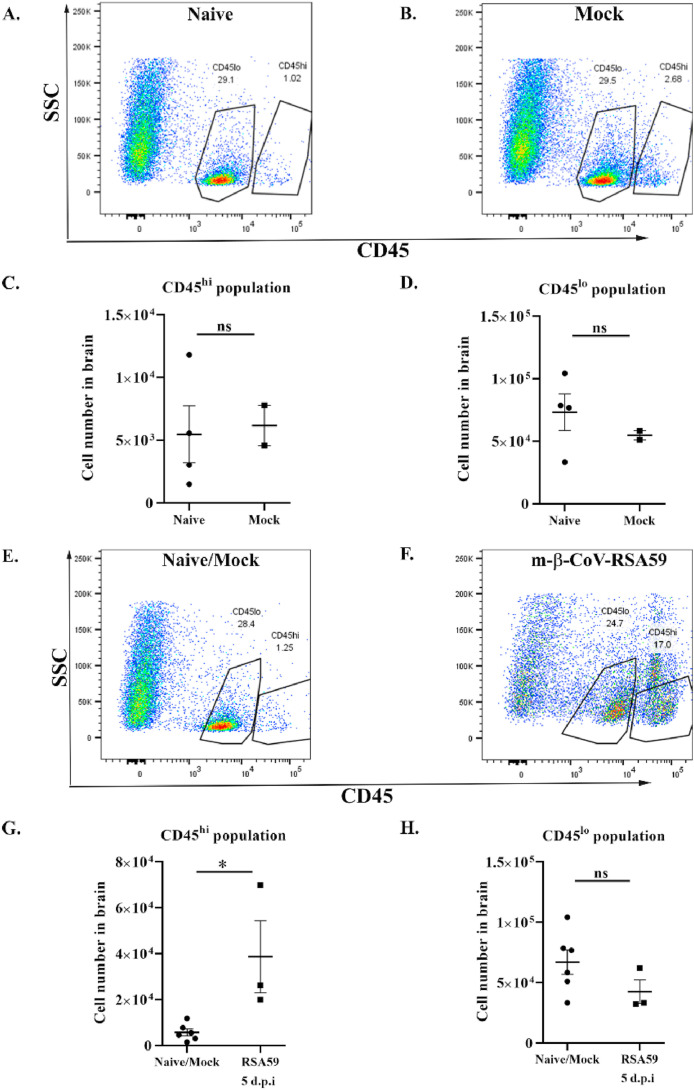
Fig. 6.
Intracranial infection with m-β-CoV-RSA59 induced higher levels of infiltrating CD45hipopulations in the brain at 5 days post-infection. Brains from age-matched naïve or mock-infected and virus-infected (day 5) mice were harvested for flow cytometric analysis. A–B: Representative flow cytometry plots indicating percentages of CD45hi and CD45lo cells in brains after gating on live cells in age-matched naïve and mock samples. C–D: Age-matched naïve or mock-infected mice did not exhibit any difference in the presence of CD45hi and CD45lo populations. E–F: Representative flow cytometry plots indicating percentages of CD45hi and CD45lo cells in brains after gating on live cells. G–H: The number of cells in the brain are graphically represented for better comparison between naïve/mock and m-β-CoV infected mice. Graphs represent data from three to six biological replicates. Asterix (*) denotes differences that are statistically significant by Student's unpaired t-test analysis (*, p < 0.05).