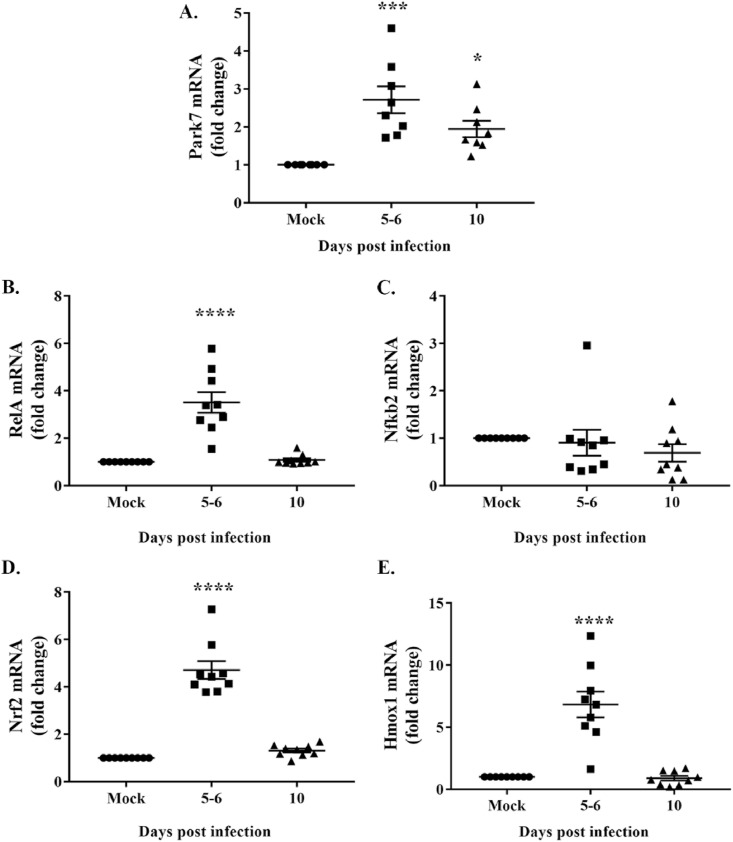
Fig. 9.
Upregulation of gene transcripts involved in oxidative and antioxidative pathways during m-β-CoV-RSA59 infection. Total RNA isolated from brain samples of mice infected with m-β-CoV-RSA59 (25000 PFU) or mock-infected was subjected to cDNA synthesis, and subsequently, RT-qPCR was performed. A: Data analysis revealed elevated mRNA levels of Park7 during acute (5–6 d.p.i) and acute-chronic (10 d.p.i) disease phase. B: Upregulation of mRNA was detected for RelA, a subunit of the NF-kB transcription factor. C: In contrast, no change was observed in the mRNA level of Nfkb2, a negative regulator of NF-kB. D–E: Moreover, m-β-CoV-RSA59 infection also induced increased transcription of antioxidative Nrf2 and Hmox1 genes. Data shown are mean ± SEM from two independent experiments. A significant difference between multiple groups was compared with ordinary one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnet's test. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001).