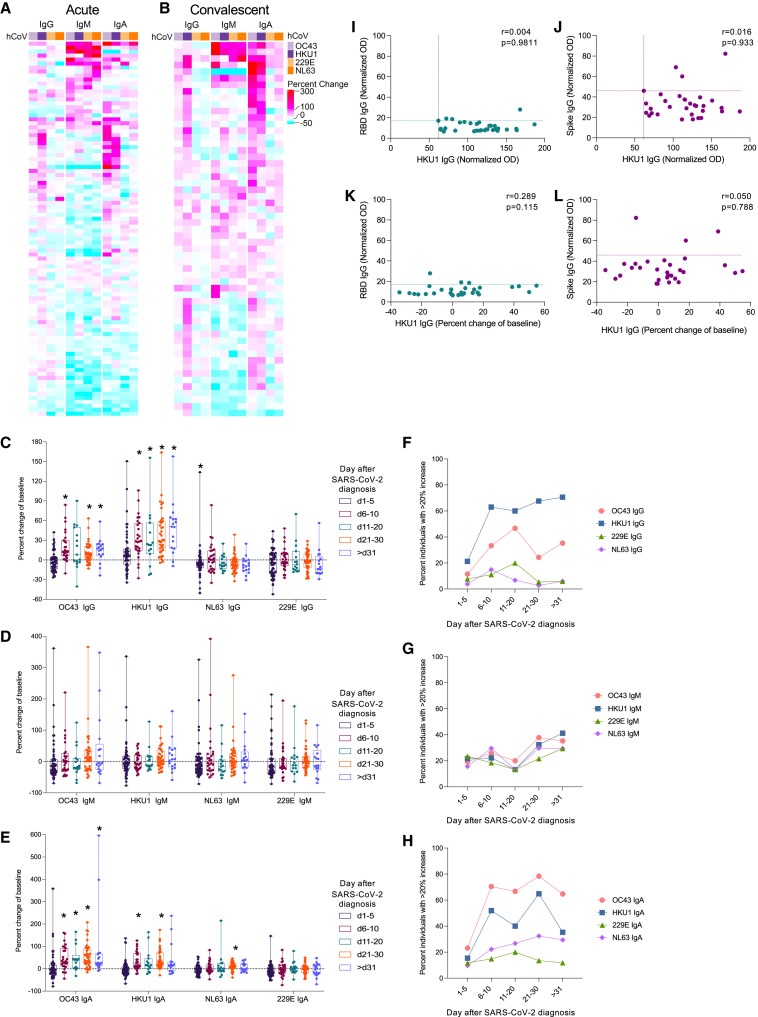
Figure 3.
Antibodies specific for OC43 and HKU1 increase following SARS-CoV-2 infection
(A and B) Samples taken from individuals during the (A) acute (1–20 days) or the (B) convalescent (>20 days) phase after PCR-confirmed infection were analyzed by ELISA for IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies specific for spike proteins of OC43, HKU1, 229E, and NL63. The percent change of the normalized OD in the sample after infection relative to the baseline is depicted in the heatmap.
(C–E) The percent change of (C) IgG, (D) IgM, and (E) IgA antibodies relative to the baseline sample was calculated for samples at indicated times following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Asterisks indicate significant difference compared to no fold change determined by Wilcoxon signed-rank test with the Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli method.
(F–H) Proportion of individuals with greater than a 20% increase in (F) IgG, (G) IgM, or (H) IgA. Fold change of hCCCoV antibodies for all acute and convalescent samples compared to baseline samples are reported in Table S2.
(I–L) Normalized OD of (I and K) SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG and (J and L) spike IgG in samples collected within 5 days of SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis were compared to the (I,J) normalized OD of HKU1 IgG in the same sample or the (K,L) boost in HKU1 IgG in the sample relative to baseline. The r value computed by the Spearman method is shown. Dashed lines indicate cut-offs for positive values.