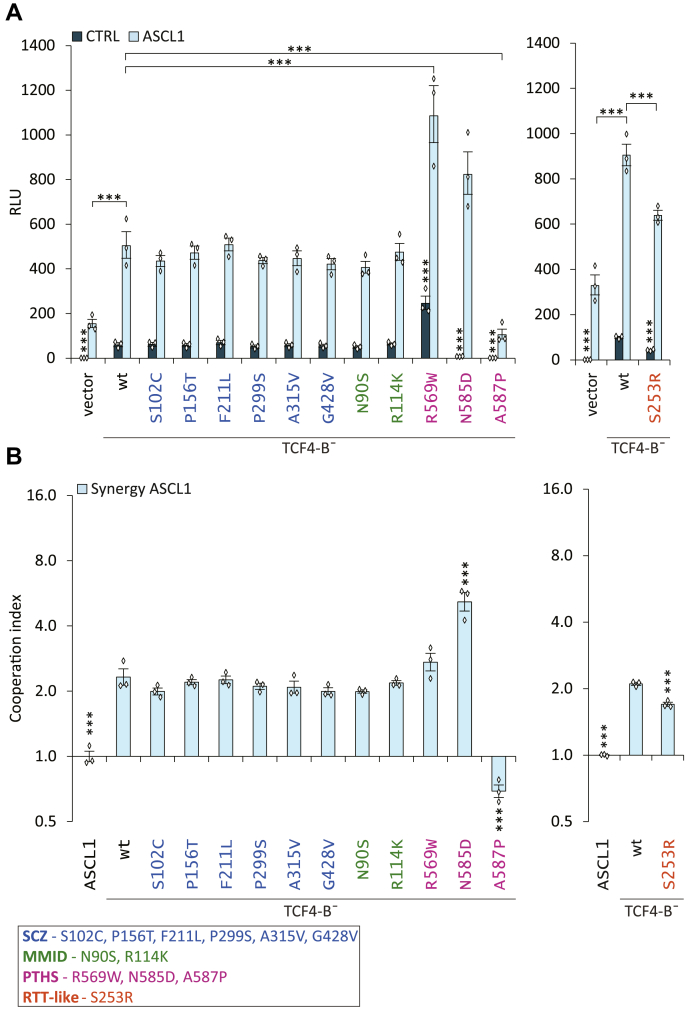
Figure 5.
Missense mutations associated with PTHS alter the ability of TCF4 to activate transcription in HEK293 cells.A, luciferase reporter assay with WT or mutant TCF4-B¯. The cells were cotransfected with WT or mutant TCF4-B¯ vectors alone or together with ASCL1, firefly luciferase reporter construct carrying 12 μE5 E-box regulatory sequences (CACCTG) in front of the minimal promoter and Renilla luciferase construct with PGK promoter for normalization. B, index of cooperation between TCF4-B¯ (WT or mutant) and ASCL1 calculated from data in (A). Four (SCZ-associated variations) or three (MMID-, PTHS, and RTT-like syndrome-associated mutations) independent experiments were performed in duplicates. The luciferase data is presented as fold-induced levels above the signals measured from empty vector-transfected (vector) untreated cells. The error bars indicate SEM. For statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA (SCZ, MMID, and PTHS mutants F (25, 50) = 258.2 p, < 0.0001; RTT-like syndrome mutant F (1.529, 4.586) = 821.5 p, < 0.0001) followed by Holm–Sidak's multiple comparisons test (A) or one-way ANOVA (SCZ, MMID, and PTHS mutants F (12, 24) = 59.52 p, < 0.0001; RTT-like syndrome mutant F (5, 10) = 1166 p, < 0.0001) followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test (B) was used. The individual data points are shown as white diamonds. Statistical significance is shown with asterisks and is relative to the cells overexpressing WT TCF4-B¯ or between the bars connected with lines; ∗∗∗p, < 0.001. MMID, Mild-to-moderate intellectual disability; PTHS, Pitt-Hopkins syndrome; RLU, relative luciferase units; RTT-like, Rett-like syndrome; SCZ, Schizophrenia; TCF4, transcription factor 4.