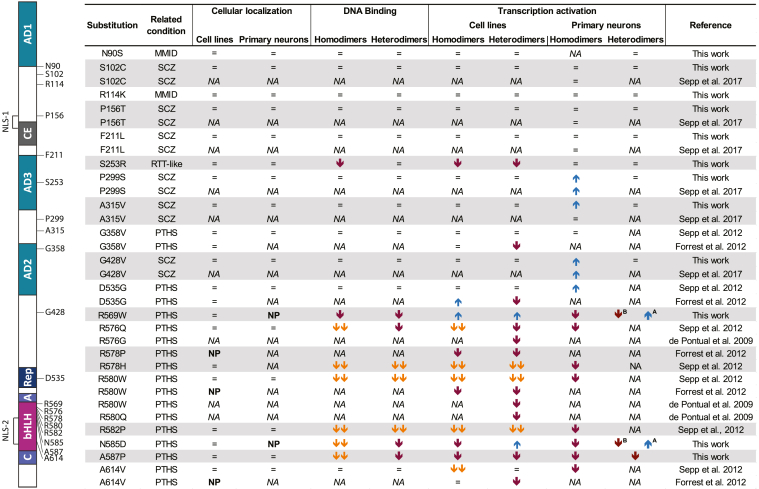
Figure 7.
Summary of the effects of amino acid substitutions on the functionality of TCF4. The effects of TCF4 amino acid substitutions on cellular localization, DNA binding, and transcription activation alone or together with ASCL1 are shown. Upwards and downwards arrows denote an increase or decrease in protein function, and "=" denotes no change. Two downwards arrows mark dominant negative effects. A or B next to arrows indicate a change specific for TCF4-A¯ or TCF4-B¯. The positions of amino acids affected by disease-related missense mutations and the variations in TCF4-B¯ are shown on the left. For more details, see the legend of Figure 1A. MMID, Mild-to-moderate intellectual disability; NA, not analysed; NP, nuclear punctae; PTHS, Pitt-Hopkins syndrome; RTT-like, Rett-like syndrome; SCZ, Schizophrenia; TCF4, transcription factor 4.