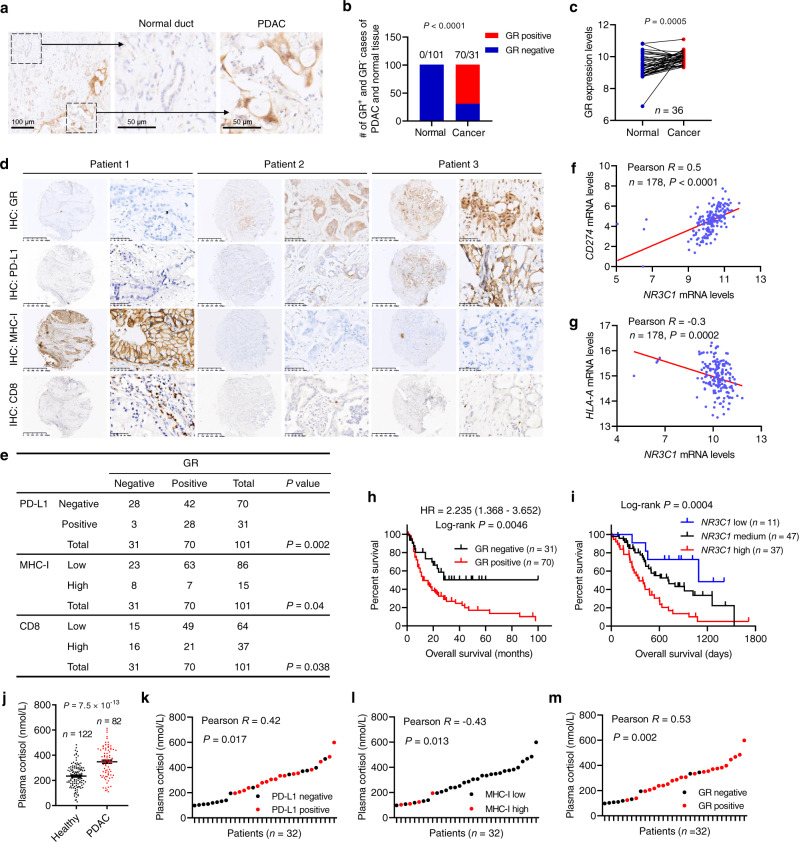
Fig. 8. GR correlates with PD-L1 expression, low MHC-I expression, and poor survival in human PDAC.
a Representative immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of GR in the normal pancreatic duct and PDAC. Scale bars, 100 μm (left), 50 μm (middle), and 50 μm (right). b Quantification of GR-positive and GR-negative cases of PDAC and adjacent normal pancreatic tissue. n = 101 patients. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed Fisher’s exact test. c GR (encoded by NR3C1) mRNA levels in paired normal pancreatic tissue and PDAC based on the GSE15471 dataset. n = 36 patients. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed paired t-test. d, e Representative IHC staining (d) and statistical analysis (e) of the correlation of GR protein levels with PD-L1, MHC-I, and CD8 proteins levels in patients with PDAC. n = 101 patients. f, g Correlation of NR3C1 (encoding GR) mRNA levels with CD274 (encoding PD-L1; f) and HLA-A (g) mRNA levels in PDAC based on TCGA data. n = 178 patients. h Kaplan–Meier curves of overall survival of pancreatic cancer patients stratified by GR protein levels based on IHC. n = 101 patients. i Kaplan–Meier curves of overall survival of pancreatic patients stratified by GR (encoded by NR3C1) mRNA levels. Data were obtained from the ICGC (International Cancer Genome Consortium). n = 95 patients. Statistical significance was determined by the log-rank test in h and i. j Plasma cortisol levels in healthy volunteers (n = 122) and PDAC patients (n = 82). Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed unpaired t-test. Error bars are s.e.m. k–m Correlation of plasma cortisol levels with PD-L1 (k), MHC-I (l), or GR (m) protein levels in pancreatic tumors. n = 32 patients. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed Pearson correlation test in e–g and k–m. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.