Figure 7. Absent PKARIα (protein kinase A type I‐α regulatory subunit) oxidation in PKARIα knock‐in (KI) following transverse aortic constriction (TAC).
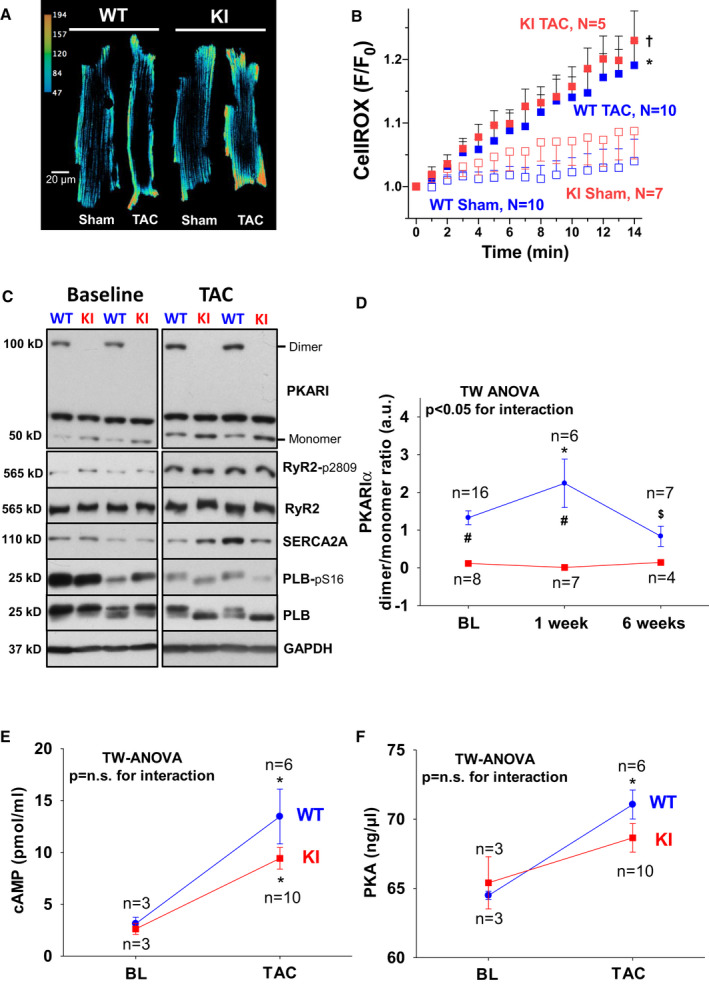
Original traces (A) and mean data (B) of CellROX‐loaded isolated ventricular myocytes from wild‐type (WT) (left panel) and KI (right panel) following sham and TAC surgery imaged every minute for 13 minutes by confocal microscopy. F/F0 indicates the fluorescence intensity normalized to baseline fluorescence. For improved visualization, gray scale values were converted to color using the depicted calibration bar. TAC induced cytosolic ROS to a similar extent in WT and KI myocytes as depicted in (B). Data are normally distributed (Shapiro‐Wilk test). *Indicates significance vs KI sham. †Indicates significance vs WT sham (using 2‐way [TW] ANOVA mixed‐effects model with Tukey post‐test). C, Original Western blots depict PKARIα dimer formation in WT hearts at baseline (BL) (upper left panel) and following TAC (upper right panel) that is completely absent in KI samples. Bottom panels in (C) depict representative Western blots of important protein kinase A (PKA)‐dependent target proteins including the RyR2 (ryanodine receptor type 2) (and PKA‐specific phosphorylation at serine 2809), SERCA2a (SR Ca ATPase 2a), and PLB (phospholamban) (and PKA‐specific phosphorylation at serine 16). Mean data for PKARIα oxidation (ie, dimer to monomer ratio) are given in (D). E, A TAC‐related increase in cAMP (3',5'‐cyclic adenosine monophosphate) was observed to a similar extent in WT and KI hearts. F, Comparable activity of PKA following TAC between groups. D, Data are normally distributed (D'Agostino‐Pearson test). Two‐way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post‐test. E and F, Data are normally distributed (Shapiro‐Wilk test). Two‐way ANOVA with Holm‐Sidak post‐test. *Indicates significance vs baseline. #Indicates significance vs WT. $Indicates significance vs previous phase. GAPDH indicates glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; and n.s., not significant.
