Figure 3. The estrogen receptor α (ERα) and the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) are recruited to a functional estrogen responsive element (ERE)/glucocorticoid responsive element (GRE) located in the promoter of the 5‐HTR2B (5‐HTR2 subtype B) gene.
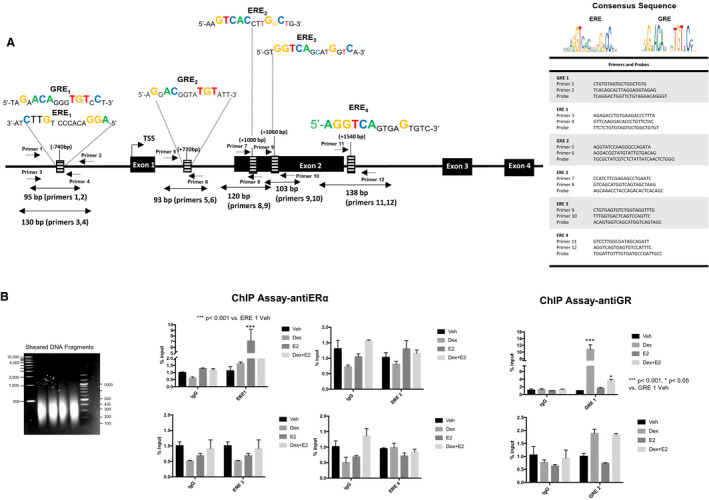
A, Schematic representation of the mouse 5‐HTR2B gene. Sequences of the consensus EREs and GREs identified within the predicted promoter, targeting areas of the designed primers, and the gene sequence of 5‐HTR2B. The table displaying the sequences of the primers and probes used for the assay. B, HL‐1 cells were treated with vehicle (Veh; black bars), 100 nmol/L dexamethasone (Dex; gray bars), 10 nmol/L estrogen (E2; dark gray bars), or dexamethasone+estrogen (Dex+E2; light gray bars) for 2 hours, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were performed with equivalent amounts of rabbit immunoglobulin G or rabbit anti‐GR or ERα antibody. Coimmunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by real‐time polymerase chain reaction using primers and probes to the identified EREs and GREs located in the 5‐HTR2B promoter and gene sequence. Sheared DNA fragment sizes were between 200 and 500 bp (left panel). Results are plotted as a function of input DNA. Percentage input was calculated using the following equations: adjusted input 100%=(Ct input−6.64) and 100*2(Adjusted input−Ct (input)). Ordinary 1‐way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparisons analysis was used to evaluate differences among group treatments unless otherwise specified. Data represent mean±SE for 4 independent experiments per treatment group. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001 vs vehicle in each group.
