Figure 3. Role of p53 in apoptosis induced by PHD (prolyl hydroxylase domain) inhibition using CoCl2 in cultured rat cardiomyocytes.
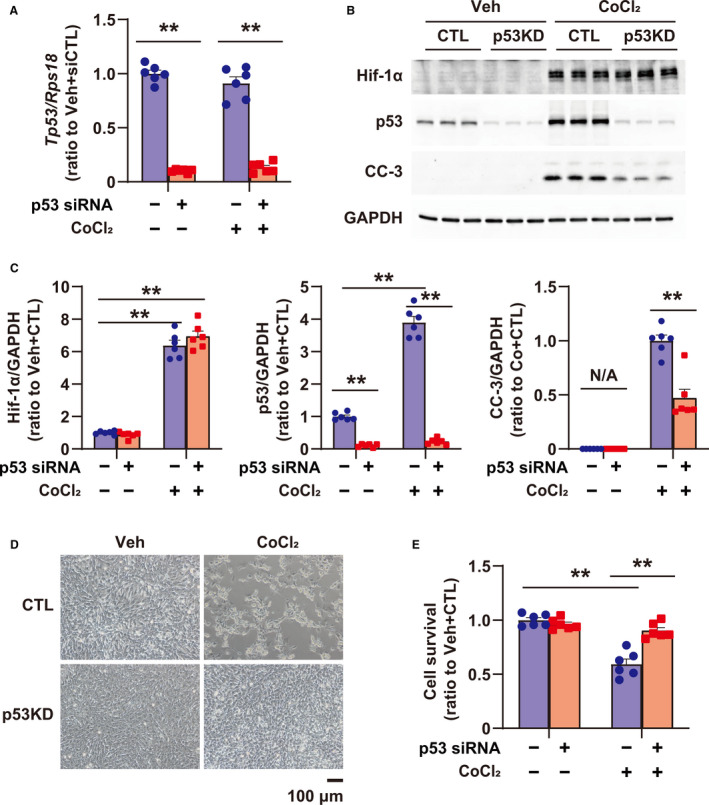
A, Tp53 expression in cultured cardiomyocytes, treated with vehicle (Veh) and CoCl2 (500 μmol/L) for 24 hours, or transfected with small interfering RNA (siRNA) for control (CTL) (scramble siRNA, CTL) and p53, was quantified by quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction; n=6 in each group. B, Expression of Hif‐1α, p53, and CC‐3 (cleaved caspase 3) in cardiomyocytes treated with Veh and CoCl2 (500 μmol/L) for 24 hours, or transfected with siRNA for CTL (scramble siRNA, CTL) and p53. GAPDH (glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase) was used as a loading CTL. C, Quantification of Western blots shown in (B); n=6 in each group. Data are shown as a ratio to the average of Veh+CTL. D, Images of cardiomyocytes treated with Veh and CoCl2 (500 μmol/L), or transfected with siRNA for CTL (scramble siRNA, CTL) and p53. E, Cellular viability using cultured cardiomyocytes treated with Veh and CoCl2 (500 μmol/L), or transfected with siRNA for CTL (scramble siRNA, CTL) and p53 by CellTiterBlue Assay; n=6 in each group. **P<0.01, analyzed by 1‐way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc test. KD indicates knockdown; and N/A, not applicable.
