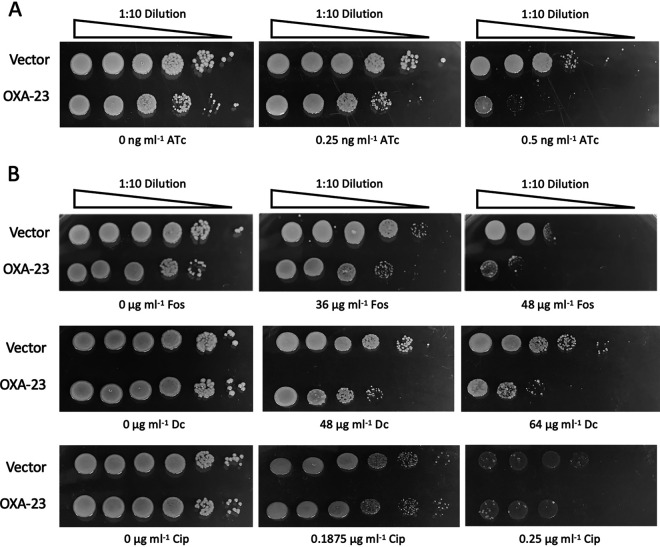
FIG 3.
Synergistic lethality of OXA-23 overexpression and a CRISPRi murA knockdown or chemical inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis enzymes. (A) Cells of ATCC 17978 Tn7::dCas9 pJE53::murA-sgRNA pQF1266-hyg (vector) or ATCC 17978 Tn7::dCas9 pJE53::murA-sgRNA pQF1266-hyg::blaOXA-23 were spotted on LB agar plates supplemented with 30 μg/ml KAN, 150 μg/ml HYG and 0, 0.25, or 0.5 ng ml−1 anhydrotetracycline (ATc) to induce murA sgRNA expression. OXA-23 β-lactamase and dCas9 genes are constitutively expressed in these strains. murA knockdown at 1 ng ml−1 ATc was lethal for both strains (data not shown). (B) Cells of ATCC 17978 Tn7::dCas9 pQF1266-hyg (vector) or ATCC 17978 Tn7::dCas9 pQF1266-hyg::blaOXA-23 were spotted on LB agar plates supplemented with 150 μg/ml HYG and 0, 3, 6, or 48 μg/ml fosfomycin (Fos; MurA inhibitor), 0, 48, or 64 μg ml−1 d-cycloserine (Dc), dual alanine racemase Alr and d-alanine:d-alanine ligase Ddl inhibitor) or 0, 0.1875, or 0.25 μg/ml ciprofloxacin (CIP; dual DNA topoisomerase and DNA gyrase inhibitor). OXA-23 β-lactamase and dCas9 genes are constitutively expressed in these strains. Bacterial growth completely inhibited for both strains at 72 μg/ml Fos, 128 μg/ml Dc, and 0.5 μg/ml CIP (data not shown).