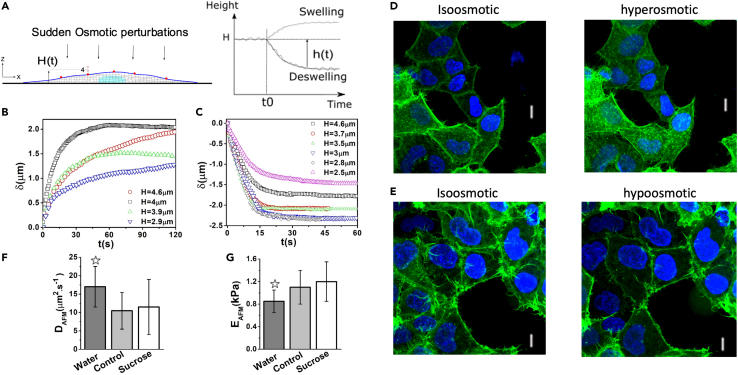
Figure 2.
Swelling/deswelling experiments and effects of hypo or hyperosmotic shock on F-actin organization
(A) By changing the osmolarity of the extracellular medium, osmotic pressure gradients were induced across the cell membrane. The pressure gradient direction (hypo or hyperosmotic shock) drives water in or out of the cell causing swelling or deswelling (a deswelling case is depicted in this schematic) and changes in bead height.
(B and C) Temporal changes in the height of HeLa cells under hypoosmotic (B) and hyperosmotic (C) shocks.
(D and E) Images of F-actin structures before and after 30 min application of osmotic perturbation. Images are maximum projections of confocal stacks of cells expressing Life-act ruby (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 34,332 (blue). Scale bars = 10μm.
(F and G) The diffusion constant and elastic modulus of cells obtained by AFM indentation tests on cells after application of osmotic changes. Error bars indicate the standard deviation in all graphs. To test pairwise differences in population experiments, Student's t-test was performed and values of p < 0.01 were considered significant and are indicated by stars.